Development of an integrated and comprehensive clinical trial process management system
- PMID: 37024877
- PMCID: PMC10078087
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-023-02158-8
Development of an integrated and comprehensive clinical trial process management system
Abstract
Background: The process of initiating and completing clinical drug trials in hospital settings is highly complex, with numerous institutional, technical, and record-keeping barriers. In this study, we independently developed an integrated clinical trial management system (CTMS) designed to comprehensively optimize the process management of clinical trials. The CTMS includes system development methods, efficient integration with external business systems, terminology, and standardization protocols, as well as data security and privacy protection.
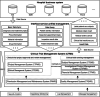
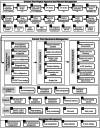
Methods: The development process proceeded through four stages, including demand analysis and problem collection, system design, system development and testing, system trial operation, and training the whole hospital to operate the system. The integrated CTMS comprises three modules: project approval and review management, clinical trial operations management, and background management modules. These are divided into seven subsystems and 59 internal processes, realizing all the functions necessary to comprehensively perform the process management of clinical trials. Efficient data integration is realized through extract-transform-load, message queue, and remote procedure call services with external systems such as the hospital information system (HIS), laboratory information system (LIS), electronic medical record (EMR), and clinical data repository (CDR). Data security is ensured by adopting corresponding policies for data storage and data access. Privacy protection complies with laws and regulations and de-identifies sensitive patient information.
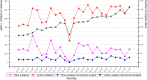
Results: The integrated CTMS was successfully developed in September 2015 and updated to version 4.2.5 in March 2021. During this period, 1388 study projects were accepted, 43,051 electronic data stored, and 12,144 subjects recruited in the First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine.
Conclusion: The developed integrated CTMS realizes the data management of the entire clinical trials process, providing basic conditions for the efficient, high-quality, and standardized operation of clinical trials.
Keywords: Clinical trial; Clinical trial management system (CTMS); Information technology; Integrated management system; Medical informatics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Utilization of a Clinical Trial Management System for the Whole Clinical Trial Process as an Integrated Database: System Development.J Med Internet Res. 2018 Apr 24;20(4):e103. doi: 10.2196/jmir.9312. J Med Internet Res. 2018. PMID: 29691212 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Clinical Trial Management System: Establishment and Efficiency Assessment.Biol Pharm Bull. 2025;48(6):782-790. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b25-00110. Biol Pharm Bull. 2025. PMID: 40467481
-
Re-engineering a Clinical Trial Management System Using Blockchain Technology: System Design, Development, and Case Studies.J Med Internet Res. 2022 Jun 27;24(6):e36774. doi: 10.2196/36774. J Med Internet Res. 2022. PMID: 35759315 Free PMC article.
-
Oncology Research: Clinical Trial Management Systems, Electronic Medical Record, and Artificial Intelligence.Semin Oncol Nurs. 2020 Apr;36(2):151005. doi: 10.1016/j.soncn.2020.151005. Epub 2020 Apr 4. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2020. PMID: 32253050 Review.
-
A review of electronic medical record keeping on mobile medical service trips in austere settings.Int J Med Inform. 2017 Feb;98:33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2016.11.008. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Int J Med Inform. 2017. PMID: 28034410 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

