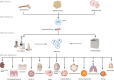
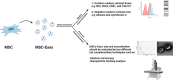
Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes in clinical trials
- PMID: 37024925
- PMCID: PMC10079493
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-023-03287-7
Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes in clinical trials
Abstract
Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (MSCs) are widely utilized in cell therapy because of their robust immunomodulatory and regenerative properties. Their paracrine activity is one of the most important features that contribute to their efficacy. Recently, it has been demonstrated that the production of various factors via extracellular vesicles, especially exosomes, governs the principal efficacy of MSCs after infusion in experimental models. Compared to MSCs themselves, MSC-derived exosomes (MSC-Exos) have provided significant advantages by efficiently decreasing unfavorable adverse effects, such as infusion-related toxicities. MSC-Exos is becoming a promising cell-free therapeutic tool and an increasing number of clinical studies started to assess the therapeutic effect of MSC-Exos in different diseases. In this review, we summarized the ongoing and completed clinical studies using MSC-Exos for immunomodulation, regenerative medicine, gene delivery, and beyond. Additionally, we summarized MSC-Exos production methods utilized in these studies with an emphasis on MSCs source, MSC-Exos isolation methods, characterization, dosage, and route of administration. Lastly, we discussed the current challenges and future directions of exosome utilization in different clinical studies as a novel therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: Clinical trials; Exosomes; Extracellular vesicles; MSC; Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential competing interest was disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles: regenerative and immunomodulatory effects and potential applications in sepsis.Cell Tissue Res. 2018 Oct;374(1):1-15. doi: 10.1007/s00441-018-2871-5. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Cell Tissue Res. 2018. PMID: 29955951 Review.
-
Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Autoimmune Diseases.Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 27;12:749192. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.749192. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34646275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for clinical use.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019 Aug;54(Suppl 2):789-792. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0616-z. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31431712 Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 21;9:816656. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.816656. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35386912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A scaffold laden with mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for promoting endometrium regeneration and fertility restoration through macrophage immunomodulation.Acta Biomater. 2020 Sep 1;113:252-266. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.06.029. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32574858
Cited by
-
Exosome-based cell therapy for diabetic foot ulcers: Present and prospect.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 11;10(20):e39251. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39251. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39498056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies to improve the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicle (MSC-EV): a promising cell-free therapy for liver disease.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Dec 13;11:1322514. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1322514. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38155924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem Cell and Regenerative Therapies for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 2;25(9):4979. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094979. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide rejuvenates septic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.World J Stem Cells. 2025 Feb 26;17(2):96893. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i2.96893. World J Stem Cells. 2025. PMID: 40061269 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes From Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Oxidative Stress-Induced POI by Regulating Autophagic Homeostasis Through the AMPK Pathway.Reprod Med Biol. 2025 May 26;24(1):e12658. doi: 10.1002/rmb2.12658. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Reprod Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40433109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trento C, Bernardo ME, Nagler A, Kuçi S, Bornhäuser M, Köhl U, et al. Manufacturing mesenchymal stromal cells for the treatment of graft-versus-host disease: A Survey among Centers Affiliated with the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018;24(11):2365–2370. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.07.015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deng K, Lin DL, Hanzlicek B, Balog B, Penn MS, Kiedrowski MJ, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and their secretome partially restore nerve and urethral function in a dual muscle and nerve injury stress urinary incontinence model. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015;308(2):F92–F100. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00510.2014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources