Risk factors of non-sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer with 1-2 sentinel lymph node macrometastases underwent total mastectomy: a case-control study
- PMID: 37024930
- PMCID: PMC10077622
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-023-02888-z
Risk factors of non-sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer with 1-2 sentinel lymph node macrometastases underwent total mastectomy: a case-control study
Abstract
Background: The randomized trials which include ACOSOG Z0011 and IBCSG 23-01 had found that the survival rates were not different in patients with cT1/2N0 and 1-2 sentinel lymph node (SLN)-positive, macro/micrometastases who underwent breast-conserving therapy, and micrometastases who underwent total mastectomy (TM), when axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) was omitted. However, for patients with cT1/2N0 and 1-2 SLN macrometastases who underwent TM; there was still insufficient evidence from clinical studies to support whether ALND can be exempted. This study aimed to investigate the risk factors of non-sentinel lymph node (nSLN) metastasis in breast cancer patients with 1-2 SLN macrometastases undergoing TM.
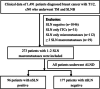
Methods: The clinicopathological data of 1491 breast cancer patients who underwent TM and SLNB from January 2017 to February 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to analyze the risk factors for nSLN metastasis.
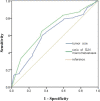
Results: A total of 273 patients with 1-2 SLN macrometastases who underwent TM were enrolled. Postoperative pathological data showed that 35.2% patients had nSLN metastasis. The results of multivariate analysis indicated that tumor size (TS) (P = 0.002; OR: 1.051; 95% CI: 1.019-1.084) and ratio of SLN macrometastases (P = 0.0001; OR: 12.597: 95% CI: 4.302-36.890) were the independent risk factors for nSLN metastasis in breast cancer patients with 1-2 SLN macrometastases that underwent TM. The ROC curve analysis suggested that when TS ≤22 mm and ratio of SLN macrometastases ≤0.33, the incidence of nSLN metastasis could be reduced to 17.1%.
Conclusions: The breast cancer patients with cT1/2N0 stage, undergoing TM and 1-2 SLN macrometastases, when the TS ≤22 mm and macrometastatic SLN does not exceed 1/3 of the total number of detected SLN, the incidence of nSLN metastasis is significantly reduced, but whether ALND can be exempted needs further exploration.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Macrometastasis; Non-sentinel lymph node; Risk factor; Sentinel lymph node; Total mastectomy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Positive non-sentinel axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer with 1-2 sentinel lymph node metastases.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Nov;97(44):e13015. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013015. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30383658 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in axillary treatment for breast cancer patients undergoing sentinel lymph node biopsy as determined by a questionnaire from the Japanese Breast Cancer Society.Breast Cancer. 2017 May;24(3):427-432. doi: 10.1007/s12282-016-0721-4. Epub 2016 Aug 23. Breast Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27553957
-
Does the presence of sentinel lymph node macrometastases in breast cancer patients require axillary lymph node dissection?-Single-center analysis.Breast J. 2018 Sep;24(5):724-729. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12997. Epub 2018 Feb 24. Breast J. 2018. PMID: 29476570
-
A quantitative analysis of tumour characteristics in breast cancer patients with extranodal extension in non-sentinel nodes.Breast. 2018 Apr;38:171-174. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Feb 3. Breast. 2018. PMID: 29413405 Review.
-
Lymphovascular invasion is a significant risk factor for non-sentinel nodal metastasis in breast cancer patients with sentinel lymph node (SLN)-positive breast cancer: a cross-sectional study.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 Dec 14;21(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-03273-6. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38097994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive and Prognostic Values of Glycoprotein 96, Androgen Receptors, and Extranodal Extension in Sentinel Lymph Node-Positive Breast Cancer: An Immunohistochemical Retrospective Study.J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 16;13(24):7665. doi: 10.3390/jcm13247665. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39768587 Free PMC article.
-
Non-sentinel lymph node metastases risk factors in patients with breast cancer with one or two sentinel lymph node macro-metastases.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 24;9(11):e21254. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21254. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37964832 Free PMC article.
-
A new prediction nomogram of non-sentinel lymph node metastasis in cT1-2 breast cancer patients with positive sentinel lymph nodes.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 26;14(1):9596. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60198-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38671007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giuliano AE, Ballman KV, McCall L, et al. Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: The ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama-J Am Med Assoc. 2017;318(10):918–926. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.11470. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Galimberti V, Cole BF, Viale G. Axillary dissection versus no axillary dissection in patients with breast cancer and sentinel-node micrometastases (IBCSG 23-01): 10-year follow-up of a randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:1385–1393. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30380-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Donker M, van Tienhoven G, Straver ME, et al. Radiotherapy or surgery of the axilla after a positive sentinel node in breast cancer (EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:1303–1310. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70460-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

