The tumor ecosystem in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and advances in ecotherapy
- PMID: 37024932
- PMCID: PMC10077663
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-023-01769-z
The tumor ecosystem in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and advances in ecotherapy
Abstract
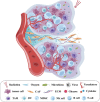
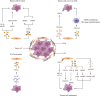
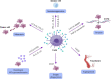
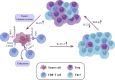
The development of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a multi-step process, and its survival depends on a complex tumor ecosystem, which not only promotes tumor growth but also helps to protect tumor cells from immune surveillance. With the advances of existing technologies and emerging models for ecosystem research, the evidence for cell-cell interplay is increasing. Herein, we discuss the recent advances in understanding the interaction between tumor cells, the major components of the HNSCC tumor ecosystem, and summarize the mechanisms of how biological and abiotic factors affect the tumor ecosystem. In addition, we review the emerging ecological treatment strategy for HNSCC based on existing studies.
Keywords: Ecological therapy; Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; Tumor ecosystem.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of nanotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by targeting tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2023 May 24;14:1189323. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1189323. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37292204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: An updated review.Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2022;33:100649. doi: 10.1016/j.ctarc.2022.100649. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 36279709 Review.
-
Immune Escape Mechanisms and Their Clinical Relevance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 24;21(19):7032. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197032. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32987799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identity matters: cancer stem cells and tumour plasticity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2023 Feb 6;25:e8. doi: 10.1017/erm.2023.4. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36740973 Review.
-
Immune deserts in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A review of challenges and opportunities for modulating the tumor immune microenvironment.Oral Oncol. 2021 Sep;120:105420. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2021.105420. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Oral Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34218062 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Microenvironmental Components in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Pers Med. 2023 Nov 17;13(11):1616. doi: 10.3390/jpm13111616. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 38003931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia inducible factor-1ɑ as a potential therapeutic target for osteosarcoma metastasis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 24;15:1350187. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1350187. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38327979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of HNSC and pulmonary metastasis using the anti-helminthic drug niclosamide to modulate Stat3 signaling activity.J Cancer. 2024 Jun 11;15(13):4406-4416. doi: 10.7150/jca.95682. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38947381 Free PMC article.
-
Global burden of non-melanoma skin cancers among older adults: a comprehensive analysis using machine learning approaches.Sci Rep. 2025 May 1;15(1):15266. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99605-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40312476 Free PMC article.
-
Nomogram model based on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical characteristics to predict prognosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 15;15(3):976-990. doi: 10.62347/MKFI3976. eCollection 2025. Am J Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40226469 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82173157/Research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant
- 82161138019/Research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant
- U20A20382/Research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant
- LY22H160041/Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Provincial under Grant
- 2022ZZ001/Chinese Medicine Research Program of Zhejiang Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

