Cellular heterogeneity and stem cells of vascular endothelial cells in blood vessel formation and homeostasis: Insights from single-cell RNA sequencing
- PMID: 37025170
- PMCID: PMC10070846
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1146399
Cellular heterogeneity and stem cells of vascular endothelial cells in blood vessel formation and homeostasis: Insights from single-cell RNA sequencing
Abstract
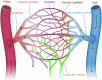
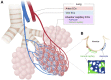
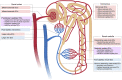
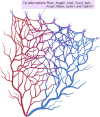
Vascular endothelial cells (ECs) that constitute the inner surface of blood vessels are essential for new vessel formation and organ homeostasis. ECs display remarkable phenotypic heterogeneity across different organs and the vascular tree during angiogenesis and homeostasis. Recent advances in single cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technologies have allowed a new understanding of EC heterogeneity in both mice and humans. In particular, scRNA-seq has identified new molecular signatures for arterial, venous and capillary ECs in different organs, as well as previously unrecognized specialized EC subtypes, such as the aerocytes localized in the alveolar capillaries of the lung. scRNA-seq has also revealed the gene expression profiles of specialized tissue-resident EC subtypes that are capable of clonal expansion and contribute to adult angiogenesis, a process of new vessel formation from the pre-existing vasculature. These specialized tissue-resident ECs have been identified in various different mouse tissues, including aortic endothelium, liver, heart, lung, skin, skeletal muscle, retina, choroid, and brain. Transcription factors and signaling pathways have also been identified in the specialized tissue-resident ECs that control angiogenesis. Furthermore, scRNA-seq has also documented responses of ECs in diseases such as cancer, age-related macular degeneration, Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis, and myocardial infarction. These new findings revealed by scRNA-seq have the potential to provide new therapeutic targets for different diseases associated with blood vessels. In this article, we summarize recent advances in the understanding of the vascular endothelial cell heterogeneity and endothelial stem cells associated with angiogenesis and homeostasis in mice and humans, and we discuss future prospects for the application of scRNA-seq technology.
Keywords: CD157/Bst1, pathological angiogenesis; angiogenesis; clonal expansion; heterogeneity; single-cell RNA sequencing; vascular endothelial cells (VECs); vascular endothelial stem cells.
Copyright © 2023 Wakabayashi and Naito.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Integrated Single-Cell Atlas of Endothelial Cells of the Human Lung.Circulation. 2021 Jul 27;144(4):286-302. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.052318. Epub 2021 May 25. Circulation. 2021. PMID: 34030460 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial cell diversity: the many facets of the crystal.FEBS J. 2024 Aug;291(15):3287-3302. doi: 10.1111/febs.16660. Epub 2022 Oct 29. FEBS J. 2024. PMID: 36266750 Review.
-
Single-cell transcriptome profiling reveals vascular endothelial cell heterogeneity in human skin.Theranostics. 2021 Apr 19;11(13):6461-6476. doi: 10.7150/thno.54917. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33995668 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting endothelial cell heterogeneity with new tools.Cell Regen. 2025 Mar 23;14(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13619-025-00223-3. Cell Regen. 2025. PMID: 40121354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping the developing human cardiac endothelium at single-cell resolution identifies MECOM as a regulator of arteriovenous gene expression.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Nov 10;118(14):2960-2972. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvac023. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 35212715 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Breast Tumor Metastasis and Its Microenvironment: It Takes Both Seed and Soil to Grow a Tumor and Target It for Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 23;16(5):911. doi: 10.3390/cancers16050911. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneity of Renal Endothelial Cells, Interact with Neighboring Cells, and Endothelial Injury in Chronic Kidney Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Apr 9;22(9):2103-2118. doi: 10.7150/ijms.108299. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40303495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell RNA-seq reveals distinct metabolic "microniches" and close host-symbiont interactions in deep-sea chemosynthetic tubeworm.Sci Adv. 2024 Jul 26;10(30):eadn3053. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adn3053. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39047091 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological premature aging of ovarian blood vessels leads to decline in fertility in middle-aged mice.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 2;16(1):72. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55509-y. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39747922 Free PMC article.
-
FLI-1-driven regulation of endothelial cells in human diseases.J Transl Med. 2024 Aug 6;22(1):740. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05546-4. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39107790 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aird W. C. (2007b). Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: II. Representative vascular beds. Circ. Res. 100, 174–190. 10.1161/01.res.0000255690.03436.ae - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

