A new biomarker combining multimodal MRI radiomics and clinical indicators for differentiating inverted papilloma from nasal polyp invaded the olfactory nerve possibly
- PMID: 37025198
- PMCID: PMC10070791
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1151455
A new biomarker combining multimodal MRI radiomics and clinical indicators for differentiating inverted papilloma from nasal polyp invaded the olfactory nerve possibly
Abstract
Background and purpose: Inverted papilloma (IP) and nasal polyp (NP), as two benign lesions, are difficult to distinguish on MRI imaging and clinically, especially in predicting whether the olfactory nerve is damaged, which is an important aspect of treatment and prognosis. We plan to establish a new biomarker to distinguish IP and NP that may invade the olfactory nerve, and to analyze its diagnostic efficacy.
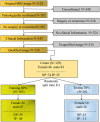
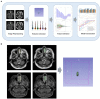
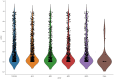
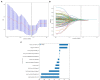
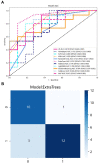
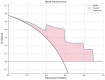
Materials and methods: A total of 74 cases of IP and 55 cases of NP were collected. A total of 80% of 129 patients were used as the training set (59 IP and 44 NP); the remaining were used as the testing set. As a multimodal study (two MRI sequences and clinical indicators), preoperative MR images including T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (T2-WI) and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (CE-T1WI) were collected. Radiomic features were extracted from MR images. Then, the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression method was used to decrease the high degree of redundancy and irrelevance. Subsequently, the radiomics model is constructed by the rad scoring formula. The area under the curve (AUC), accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) of the model have been calculated. Finally, the decision curve analysis (DCA) is used to evaluate the clinical practicability of the model.
Results: There were significant differences in age, nasal bleeding, and hyposmia between the two lesions (p < 0.05). In total, 1,906 radiomic features were extracted from T2-WI and CE-T1WI images. After feature selection, using 12 key features to bulid model. AUC, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy on the testing cohort of the optimal model were, respectively, 0.9121, 0.828, 0.9091, and 0.899. AUC on the testing cohort of the optimal model was 0.9121; in addition, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were, respectively, 0.828, 0.9091, and 0.899.
Conclusion: A new biomarker combining multimodal MRI radiomics and clinical indicators can effectively distinguish between IP and NP that may invade the olfactory nerve, which can provide a valuable decision basis for individualized treatment.
Keywords: MRI; diagnostic efficacy; inverted papilloma; nasal polyp; olfactory nerve; radiomic.
Copyright © 2023 Du, Yuan and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Classification of nasal polyps and inverted papillomas using CT-based radiomics.Insights Imaging. 2023 Nov 13;14(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01536-0. Insights Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37955767 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative Prediction of Malignant Transformation of Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma Using MR Radiomics.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 23;12:870544. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.870544. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35402254 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics Based on Multimodal MRI for the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Aug;52(2):596-607. doi: 10.1002/jmri.27098. Epub 2020 Feb 14. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32061014
-
Pretreatment MR imaging radiomics signatures for response prediction to induction chemotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Eur J Radiol. 2018 Jan;98:100-106. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.11.007. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Eur J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29279146
-
Preoperative prediction of histopathological grading in patients with chondrosarcoma using MRI-based radiomics with semantic features.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Jul 11;24(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01330-4. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38992609 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Classification of nasal polyps and inverted papillomas using CT-based radiomics.Insights Imaging. 2023 Nov 13;14(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01536-0. Insights Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37955767 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Radiomics to Predict Malignant Transformation of Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 27;17(13):2175. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132175. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards Precision Medicine in Sinonasal Tumors: Low-Dimensional Radiomic Signature Extraction from MRI.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jun 30;15(13):1675. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15131675. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647674 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence and MRI in sinonasal tumors discrimination: where do we stand?Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Mar;282(3):1557-1566. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-09169-9. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 39719474
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

