Pathogenesis, clinical features, and phenotypes of pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease: A consensus statement from the Pulmonary Vascular Research Institute's Innovative Drug Development Initiative - Group 3 Pulmonary Hypertension
- PMID: 37025209
- PMCID: PMC10071306
- DOI: 10.1002/pul2.12213
Pathogenesis, clinical features, and phenotypes of pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease: A consensus statement from the Pulmonary Vascular Research Institute's Innovative Drug Development Initiative - Group 3 Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
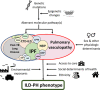
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a frequent complication of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Although PH has mostly been described in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, it can manifest in association with many other forms of ILD. Associated pathogenetic mechanisms are complex and incompletely understood but there is evidence of disruption of molecular and genetic pathways, with panvascular histopathologic changes, multiple pathophysiologic sequelae, and profound clinical ramifications. While there are some recognized clinical phenotypes such as combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema and some possible phenotypes such as connective tissue disease associated with ILD and PH, the identification of further phenotypes of PH in ILD has thus far proven elusive. This statement reviews the current evidence on the pathogenesis, recognized patterns, and useful diagnostic tools to detect phenotypes of PH in ILD. Distinct phenotypes warrant recognition if they are characterized through either a distinct presentation, clinical course, or treatment response. Furthermore, we propose a set of recommendations for future studies that might enable the recognition of new phenotypes.
Keywords: endophenotype; histology; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; pathophysiology; pulmonary vascular disease.
© 2023 The Authors. Pulmonary Circulation published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Pulmonary Vascular Research Institute.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Lucilla Piccari has received research funding from and served as a speaker for Janssen and Ferrer, advised Janssen, Ferrer and United Therapeutics as well as received support for attending congresses from Janssen, MSD and Ferrer, all of which not related to this manuscript. Prof Katerina Antoniou has a consultant role for Roche, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, GSK, honoraria for lecturing for Roche, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, GSK, Astra‐Zeneca, Chiesi & Menarini. Dr. Paul M. Hassoun serves on a scientific advisory board for Merck, an activity unrelated to the current work. Dr. Sylvia M. Nikkho is an employee of Bayer AG. Dr. Rajan Saggar has a Consulting and Advisory Role for United Therapeutics, Third Pole, Novartis, Acceleron, Aerovate, and Janssen. Dr. Oksana A. Shlobin has consulted for UT, Bayer, Altavant, Aerovate, Jenssen&Jenssen and Merck, and is on the speaker bureau for UT, Bayer, and JJ. Dr. Steven D. Nathan is a consultant for United Therapeutics, Bellerophon, Third Pole, Roche, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Merck and Daewoong. Dr. Stephen John Wort received honoraria from Janssen, MSD, Bayer and Acceleron for advisory boards; received honoraria from Janssen for educational activity, received unrestricted research grants from Janssen and Bayer, and travel grants, conference registration, and accommodation from Actelion and GSK. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hayes D, Black SM, Tobias JD, Kirkby S, Mansour HM, Whitson BA. Influence of pulmonary hypertension on patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis awaiting lung transplantation. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;101:246–52. - PubMed
-
- Judge EP, Fabre A, Adamali HI, Egan JJ. Acute exacerbations and pulmonary hypertension in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2012;40:93–100. - PubMed
-
- Kimura M, Taniguchi H, Kondoh Y, Kimura T, Kataoka K, Nishiyama O, Aso H, Sakamoto K, Hasegawa Y. Pulmonary hypertension as a prognostic indicator at the initial evaluation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respiration. 2013;85:456–63. - PubMed
-
- Hoeper MM, Behr J, Held M, Grunig E, Vizza CD, Vonk‐Noordegraaf A, Lange TJ, Claussen M, Grohé C, Klose H, Olsson KM, Zelniker T, Neurohr C, Distler O, Wirtz H, Opitz C, Huscher D, Pittrow D, Gibbs JSR. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with chronic fibrosing idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0141911. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nikkho SM, Richter MJ, Shen E, Abman SH, Antoniou K, Chung J, Fernandes P, Hassoun P, Lazarus HM, Olschewski H, Piccari L, Psotka M, Saggar R, Shlobin OA, Stockbridge N, Vitulo P, Vizza CD, Wort SJ, Nathan SD. Clinical significance of pulmonary hypertension in interstitial lung disease: a consensus statement from the Pulmonary Vascular Research Institute's innovative drug development initiative—group 3 pulmonary hypertension. Pulm Circ. 2022;12(3):1–16. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

