A Path to Real-World Evidence in Critical Care Using Open-Source Data Harmonization Tools
- PMID: 37025303
- PMCID: PMC10072311
- DOI: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000893
A Path to Real-World Evidence in Critical Care Using Open-Source Data Harmonization Tools
Abstract
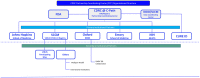
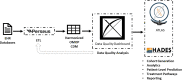
COVID-19 highlighted the need for use of real-world data (RWD) in critical care as a near real-time resource for clinical, research, and policy efforts. Analysis of RWD is gaining momentum and can generate important evidence for policy makers and regulators. Extracting high quality RWD from electronic health records (EHRs) requires sophisticated infrastructure and dedicated resources. We sought to customize freely available public tools, supporting all phases of data harmonization, from data quality assessments to de-identification procedures, and generation of robust, data science ready RWD from EHRs. These data are made available to clinicians and researchers through CURE ID, a free platform which facilitates access to case reports of challenging clinical cases and repurposed treatments hosted by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences/National Institutes of Health in partnership with the Food and Drug Administration. This commentary describes the partnership, rationale, process, use case, impact in critical care, and future directions for this collaborative effort.
Keywords: Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership (OMOP); critical care; data harmonization; drug repurposing; electronic health record; real-world data.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have disclosed that they do not have any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Concato J, Corrigan-Curay J: Real-World evidence — where are we now? N Engl J Med 2022; 386:1680–1682 - PubMed
-
- Walkey AJ, Sheldrick RC, Kashyap R, et al. : Guiding principles for the conduct of observational critical care research for coronavirus disease 2019 pandemics and beyond: The Society of Critical Care Medicine Discovery Viral Infection and Respiratory Illness Universal Study Registry. Crit Care Med 2020; 48:e1038–e1044 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peacock FW, Hauser GR, Toshev P, et al. : 59 Artificial intelligence occult sepsis detection in the emergency department: A large, multicenter real-world data study. Ann Emerg Med 2021; 78:S24
-
- Derman BA, Belli AJ, Battiwalla M, et al. : Reality check: Real-world evidence to support therapeutic development in hematologic malignancies. Blood Rev 2022; 53100913. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

