The effect of parecoxib sodium on postoperative delirium in elderly patients with hip arthroplasty
- PMID: 37025488
- PMCID: PMC10072322
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.947982
The effect of parecoxib sodium on postoperative delirium in elderly patients with hip arthroplasty
Abstract
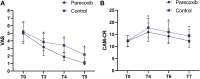
Objective: This study aimed to clarify the effect of parecoxib sodium on the occurrence of postoperative delirium and to investigate its possible mechanism. Methods: A total of 80 patients who underwent elective hip arthroplasty in our hospital between December 2020 and December 2021 were selected and randomly divided into two groups: a parecoxib sodium group (group P, n = 40) and a control group (group C, n = 40). Patients in group P were intravenously injected with 40 mg of parecoxib sodium 30 min before anesthesia and at the end of the surgery. Patients in group C were intravenously injected with the same volume of normal saline at the same time points. The primary endpoint was the incidence of POD, and the secondary endpoints were the levels of inflammatory factors (tumor necrosis factor- α [TNF-α], interleukin [IL]-1β, IL-6, and IL-10), nerve injury-related factors (brain-derived neurotrophic factor [BDNF], S-100β protein, neuron-specific enolase [NSE], and neurofilament light chain [NfL]), and antioxidant factors (heme oxygenase-1 [HO-1]), as well as the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Confusion Assessment Method-Chinese Reversion (CAM-CR) scores. Results: The incidence of POD was 10% in group P and 27.5% in group C. Intergroup comparison revealed that the levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, S-100β, NfL, and NSE were lower, and BDNF was higher, in group P than in group C at each postoperative time point. The levels of IL-6 were lower, and the levels of IL-10 and HO-1 were higher, in group P than in group C at 1 h and 1 day postoperatively (p < 0.05). Three days after surgery, the differences in the levels of IL-6, IL-10, and HO-1 were not statistically significant between the two groups (p > 0.05). The VAS and CAM-CR scores were lower at each postoperative time point in group P than in group C (p < 0.05). Conclusion: Parecoxib sodium could reduce postoperative pain, decrease the plasma levels of inflammatory and nerve injury-related factors, upregulate HO-1 levels, and reduce the incidence of POD. The results of this study suggest that parecoxib sodium may reduce the occurrence of POD through the effects of anti-inflammation, analgesia, and antioxidants.
Keywords: HO-1; anesthesiology; inflammation; parecoxib sodium; postoperative delirium.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Liu, Bai, Chen, Cui, Gao and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adamis D., van Gool W. A., Eikelenboom P. (2021). Consistent patterns in the inconsistent associations of Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), C-Reactive Protein (C-RP) and Interleukin 6 (IL-6) levels with delirium in surgical populations. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 97, 104518. 10.1016/j.archger.2021.104518 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources