Treatment strategies for clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Past, present and future
- PMID: 37025584
- PMCID: PMC10070676
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1133832
Treatment strategies for clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Past, present and future
Abstract
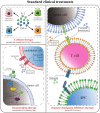
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the most prevalent histological subtype of kidney cancer, which is prone to metastasis, recurrence, and resistance to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. The burden it places on human health due to its refractory nature and rising incidence rate is substantial. Researchers have recently determined the ccRCC risk factors and optimized the clinical therapy based on the disease's underlying molecular mechanisms. In this paper, we review the established clinical therapies and novel potential therapeutic approaches for ccRCC, and we support the importance of investigating novel therapeutic options in the context of combining established therapies as a research hotspot, with the goal of providing diversified therapeutic options that promise to address the issue of drug resistance, with a view to the early realization of precision medicine and individualized treatment.
Keywords: clear cell renal cell carcinoma; cytokine; immune checkpoint inhibitor; immunological substance modification; obesity paradox; renal cancer stem cells; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Copyright © 2023 Yang, Wang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

