A study on L-threonine and L-serine uptake in Escherichia coli K-12
- PMID: 37025642
- PMCID: PMC10070963
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1151716
A study on L-threonine and L-serine uptake in Escherichia coli K-12
Abstract
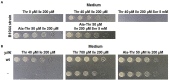
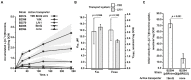
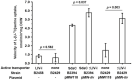
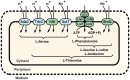
In the current study, we report the identification and characterization of the yifK gene product as a novel amino acid carrier in E. coli K-12 cells. Both phenotypic and biochemical analyses showed that YifK acts as a permease specific to L-threonine and, to a lesser extent, L-serine. An assay of the effect of uncouplers and composition of the reaction medium on the transport activity indicates that YifK utilizes a proton motive force to energize substrate uptake. To identify the remaining threonine carriers, we screened a genomic library prepared from the yifK-mutant strain and found that brnQ acts as a multicopy suppressor of the threonine transport defect caused by yifK disruption. Our results indicate that BrnQ is directly involved in threonine uptake as a low-affinity but high-flux transporter, which forms the main entry point when the threonine concentration in the external environment reaches a toxic level. By abolishing YifK and BrnQ activity, we unmasked and quantified the threonine transport activity of the LIV-I branched chain amino acid transport system and demonstrated that LIV-I contributes significantly to total threonine uptake. However, this contribution is likely smaller than that of YifK. We also observed the serine transport activity of LIV-I, which was much lower compared with that of the dedicated SdaC carrier, indicating that LIV-I plays a minor role in the serine uptake. Overall, these findings allow us to propose a comprehensive model of the threonine/serine uptake subsystem in E. coli cells.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; L-serine uptake; L-threonine uptake; amino acid transporter; transmembrane transport.
Copyright © 2023 Khozov, Bubnov, Plisov, Vybornaya, Yuzbashev, Agrimi, Messina, Stepanova, Kudina, Alekseeva, Netrusov and Sineoky.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

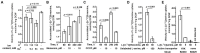
References
-
- Bubnov D. M., Yuzbashev T. V., Khozov A. A., Melkina O. E., Vybornaya T. V., Stan G.-B., et al. (2022). Robust counterselection and advanced λRed recombineering enable markerless chromosomal integration of large heterologous constructs. Nucleic Acids Res. 50, 8947–8960. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac649, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

