Benchmarking of Nanopore R10.4 and R9.4.1 flow cells in single-cell whole-genome amplification and whole-genome shotgun sequencing
- PMID: 37025654
- PMCID: PMC10070092
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.03.038
Benchmarking of Nanopore R10.4 and R9.4.1 flow cells in single-cell whole-genome amplification and whole-genome shotgun sequencing
Abstract
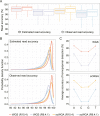
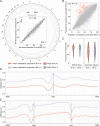
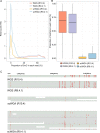
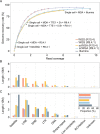
Third-generation sequencing can be used in human cancer genomics and epigenomic research. Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) recently released R10.4 flow cell, which claimed an improved read accuracy compared to R9.4.1 flow cell. To evaluate the benefits and defects of R10.4 flow cell for cancer cell profiling on MinION devices, we used the human non-small-cell lung-carcinoma cell line HCC78 to construct libraries for both single-cell whole-genome amplification (scWGA) and whole-genome shotgun sequencing. The R10.4 and R9.4.1 reads were benchmarked in terms of read accuracy, variant detection, modification calling, genome recovery rate and compared with the next generation sequencing (NGS) reads. The results highlighted that the R10.4 outperforms R9.4.1 reads, achieving a higher modal read accuracy of over 99.1%, superior variation detection, lower false-discovery rate (FDR) in methylation calling, and comparable genome recovery rate. To achieve high yields scWGA sequencing in the ONT platform as NGS, we recommended multiple displacement amplification with a modified T7 endonuclease Ⅰ cutting procedure as a promising method. In addition, we provided a possible solution to filter the likely false positive sites among the whole genome region with R10.4 by using scWGA sequencing result as a negative control. Our study is the first benchmark of whole genome single-cell sequencing using ONT R10.4 and R9.4.1 MinION flow cells by clarifying the capacity of genomic and epigenomic profiling within a single flow cell. A promising method for scWGA sequencing together with the methylation calling results can benefit researchers who work on cancer cell genomic and epigenomic profiling using third-generation sequencing.
Keywords: Long read; Methylation; Nanopore DNA sequencing; Single-cell whole genome amplification sequencing; Whole genome shotgun sequencing.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest associated with this study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Closing the gap: Oxford Nanopore Technologies R10 sequencing allows comparable results to Illumina sequencing for SNP-based outbreak investigation of bacterial pathogens.J Clin Microbiol. 2024 May 8;62(5):e0157623. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01576-23. Epub 2024 Mar 5. J Clin Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38441926 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of R9.4.1/Kit10 and R10/Kit12 Oxford Nanopore flowcells and chemistries in bacterial genome reconstruction.Microb Genom. 2023 Jan;9(1):mgen000910. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000910. Microb Genom. 2023. PMID: 36748454 Free PMC article.
-
The newest Oxford Nanopore R10.4.1 full-length 16S rRNA sequencing enables the accurate resolution of species-level microbial community profiling.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Oct 31;89(10):e0060523. doi: 10.1128/aem.00605-23. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37800969 Free PMC article.
-
Long-read sequencing in deciphering human genetics to a greater depth.Hum Genet. 2019 Dec;138(11-12):1201-1215. doi: 10.1007/s00439-019-02064-y. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31538236 Review.
-
Third-Generation Sequencing: The Spearhead towards the Radical Transformation of Modern Genomics.Life (Basel). 2021 Dec 26;12(1):30. doi: 10.3390/life12010030. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35054423 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Easing genomic surveillance: A comprehensive performance evaluation of long-read assemblers across multi-strain mixture data of HIV-1 and Other pathogenic viruses for constructing a user-friendly bioinformatic pipeline.F1000Res. 2024 May 31;13:556. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.149577.1. eCollection 2024. F1000Res. 2024. PMID: 38984017 Free PMC article.
-
Three Rounds of Read Correction Significantly Improve Eukaryotic Protein Detection in ONT Reads.Microorganisms. 2024 Jan 24;12(2):247. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12020247. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38399651 Free PMC article.
-
Benchmarking short and long read polishing tools for nanopore assemblies: achieving near-perfect genomes for outbreak isolates.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jul 8;25(1):679. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10582-x. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38978005 Free PMC article.
-
The usefulness of nanopore sequencing in whole-genome sequencing-based genotyping of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jul 2;12(7):e0050924. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00509-24. Epub 2024 May 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38809017 Free PMC article.
-
Nanopore strand-specific mismatch enables de novo detection of bacterial DNA modifications.Genome Res. 2024 Nov 20;34(11):2025-2038. doi: 10.1101/gr.279012.124. Genome Res. 2024. PMID: 39358016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schadt E.E., Turner S., Kasarskis A. A window into third-generation sequencing. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;vol. 19(R2):R227–R240. Oct 15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
