Energy transmission through carreau yasuda fluid influenced by ethylene glycol with activation energy and ternary hybrid nanocomposites by using a mathematical model
- PMID: 37025838
- PMCID: PMC10070525
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14740
Energy transmission through carreau yasuda fluid influenced by ethylene glycol with activation energy and ternary hybrid nanocomposites by using a mathematical model
Retraction in
-
Retraction notice to "Energy transmission through carreau yasuda fluid influenced by ethylene glycol with activation energy and ternary hybrid nanocomposites by using a mathematical model" [Heliyon 9 (2023) e14740].Heliyon. 2025 Sep 15;11(14):e43843. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e43843. eCollection 2025 Sep. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 41215889 Free PMC article.
Abstract
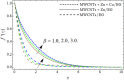
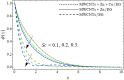
The current study aims to assess the augmentation of energy transmission in the presence of magnetic dipole through trihybrid Carreau Yasuda nanofluid flow across a vertical sheet. The rheological properties and thermal conductivity of the based fluids are improved by framing an accurate combination of nanoparticles (NPs). The trihybrid nanofluid (Thnf) has been synthesized by the addition of ternary nanocomposites (MWCNTs, Zn, Cu) to the ethylene glycol. The energy and velocity conveyance has been observed in the context of the Darcy Forchhemier effect, chemical reaction, heat source/sink, and activation energy. The trihybrid nanofluid flow across a vertical sheet has been accurately calculated for velocity, concentration, and thermal energy in the form of a system of nonlinear PDEs. The set of PDEs is reduced to dimensionless ODEs by using suitable similarity replacements. The obtained set of non-dimensional differential equations is numerically computed through the Matlab package bvp4c. It has been perceived that the energy curve enhances by the influence of heat generation factor and viscous dissipation. It is also noted that the magnetic dipole has a momentous contribution to raising the transmission of thermal energy of trihybrid nanofluid and declines the velocity curve. The inclusion of multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), zinc (Zn), and copper (Cu) nano particulates to the base fluid "ethylene glycol", augments the energy and velocity outlines.
Keywords: Activation energy; Carreau yasuda liquid; Heat source term; Magnetic dipole; Trihybrid nanofluid; bvp4c.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures













References
-
- Rashidi M.M., Rostami B., Freidoonimehr N., Abbasbandy S. Free convective heat and mass transfer for MHD fluid flow over a permeable vertical stretching sheet in the presence of the radiation and buoyancy effects. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2014;5(3):901–912.
-
- Waini I., Ishak A., Pop I. Hybrid nanofluid flow towards a stagnation point on an exponentially stretching/shrinking vertical sheet with buoyancy effects. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2020;31(1):216–235.
-
- Ali B., Hussain S., Nie Y., Ali L., Hassan S.U. Finite element simulation of bioconvection and cattaneo-Christov effects on micropolar based nanofluid flow over a vertically stretching sheet. Chin. J. Phys. 2020;68:654–670.
-
- Abbas T., Rehman S., Shah R.A., Idrees M., Qayyum M. Analysis of MHD Carreau fluid flow over a stretching permeable sheet with variable viscosity and thermal conductivity. Phys. Stat. Mech. Appl. 2020;551
-
- Sarada K., Gowda R.J.P., Sarris I.E., Kumar R.N., Prasannakumara B.C. Effect of magnetohydrodynamics on heat transfer behaviour of a non-Newtonian fluid flow over a stretching sheet under local thermal non-equilibrium condition. Fluid. 2021;6(8):264.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

