The association between peer rejection and behavior problems of migrant adolescents in China: A moderated mediation model of delinquent peer affiliation and parenting
- PMID: 37025847
- PMCID: PMC10070155
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14955
The association between peer rejection and behavior problems of migrant adolescents in China: A moderated mediation model of delinquent peer affiliation and parenting
Abstract
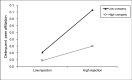
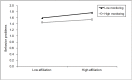
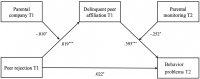
Facing a stressful environment of peer rejection and discrimination, Chinese migrant adolescents are at high risk of developing behavior problems while receiving insufficient family support. In this context, the current study aimed to explore the pathway from peer rejection to adolescent behavior problems via the mediating role of delinquent peer affiliation and with the moderating roles of parental company and parental monitoring taken into consideration. A sample of 2041 migrant adolescents (46.2% female, mean age = 13.595) was drawn from the first and second waves of the China Education Panel Survey (CEPS) for running a moderated mediation model. The results demonstrated that peer rejection positively predicted behavior problems through the mediator of delinquent peer affiliation (indirect effect = 0.007, 95% CI = [0.003, 0.014]). This mediating mechanism was moderated by parental company and by parental monitoring. Our study deepened the theoretical understanding and application of the general strain theory by showing how the interaction of peer stressors and parenting elements affected the behavior of migrant adolescents in a Chinese context. Further studies could pay more attention to the dynamic interplay between the family and peer systems, especially for rejected and marginalized adolescent groups. Limitations and implications for future school-based and family-based practices are also discussed.
Keywords: Adolescent; Behavior problems; Delinquent peer affiliation; Parenting; Peer rejection.
©2023PublishedbyElsevierLtd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peer Victimization and Aggressive Behavior Among Chinese Adolescents: Delinquent Peer Affiliation as a Mediator and Parental Knowledge as a Moderator.Front Psychol. 2018 Jun 28;9:1036. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01036. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 30002637 Free PMC article.
-
Parenting behaviors and deviant peer affiliation among Chinese adolescents: the mediating role of psychological reactance and the moderating role of gender.BMC Psychol. 2025 Apr 14;13(1):379. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-02703-2. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40229659 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived parental monitoring and adolescent internet addiction: A moderated mediation model.Addict Behav. 2017 Nov;74:48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2017.05.033. Epub 2017 May 27. Addict Behav. 2017. PMID: 28575738
-
School climate and delinquency among Chinese adolescents: analyses of effortful control as a moderator and deviant peer affiliation as a mediator.J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2015 Jan;43(1):81-93. doi: 10.1007/s10802-014-9903-8. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2015. PMID: 24962709
-
A Developmental Perspective on Peer Rejection, Deviant Peer Affiliation, and Conduct Problems Among Youth.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2015 Dec;46(6):823-38. doi: 10.1007/s10578-014-0522-y. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2015. PMID: 25410430 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Steinberg L., Silk J.S. Handbook of Parenting: Children and Parenting. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers; 2002. Parenting adolescents; pp. 103–133.
-
- Dodge K.A., Dishion T.J., Lansford J.E. Deviant peer influences in intervention and public policy for youth. Soc. Pol. Rep. 2006;20:1–20. doi: 10.1002/j.2379-3988.2006.tb00046.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

