A Multicenter Analysis of Nucleic Acid Quantification Using Aqueous Humor Liquid Biopsy in Retinoblastoma: Implications for Clinical Testing
- PMID: 37025945
- PMCID: PMC10070901
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xops.2023.100289
A Multicenter Analysis of Nucleic Acid Quantification Using Aqueous Humor Liquid Biopsy in Retinoblastoma: Implications for Clinical Testing
Abstract
Purpose: Retinoblastoma (RB) is most often diagnosed with clinical features and not diagnosed with tumor biopsy. This study describes tumor-derived analyte concentrations from aqueous humor (AH) liquid biopsy and its use in clinical assays.
Design: Case series study.
Participants: Sixty-two RB eyes from 55 children and 14 control eyes from 12 children from 4 medical centers.
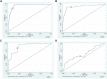
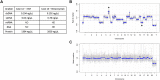
Methods: This study included 128 RB AH samples including: diagnostic (DX) samples, samples from eyes undergoing treatment (TX), samples after completing treatment (END), and during bevacizumab injection for radiation therapy after completing RB treatment (BEV). Fourteen-control AH were analyzed for unprocessed analytes (double-stranded DNA [dsDNA], single-stranded DNA [ssDNA], micro-RNA [miRNA], RNA, and protein) with Qubit fluorescence assays. Double-stranded DNA from 2 RB AH samples underwent low-pass whole-genome sequencing to detect somatic copy number alterations. Logistic regression was used to predict disease burden given analyte concentrations.
Main outcome measures: Unprocessed analyte (dsDNA, ssDNA, miRNA, RNA and protein) concentrations.
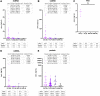
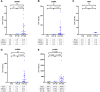
Results: Results revealed dsDNA, ssDNA, miRNA, and proteins, but not RNA, were quantifiable in most samples (up to 98%) with Qubit fluorescence assays. Median dsDNA concentration was significantly higher in DX (3.08 ng/μl) compared to TX (0.18 ng/μl; P < 0.0001) at an order of 17 times greater and 20 times greater than END samples (0.15 ng/μl; P = 0.001). Using logistic regression, nucleic acid concentrations were useful in predicting higher versus lower RB disease burden. Retinoblastoma somatic copy number alterations were identified in a TX, but not in a BEV sample, indicating the correlation with RB activity.
Conclusions: Aqueous humor liquid biopsy in RB is a high-yield source of dsDNA, ssDNA, miRNA, and protein. Diagnostic samples are most useful for RB 1 gene mutational analyses. Genomic analysis may be more informative of tumor activity status than quantification alone and can be performed even with smaller analyte concentrations obtained from TX samples.
Financial disclosures: Proprietary or commercial disclosure may be found after the references.
Keywords: Aqueous humor; Circulating analytes; Liquid biopsy; Multicenter; Retinoblastoma.
© 2023 by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. This is.
Figures

References
-
- Karcioglu Z.A., Gordon R.A., Karcioglu G.L. Tumor seeding in ocular fine needle aspiration biopsy. Ophthalmology. 1985;92:1763–1767. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

