CRISPR/Cas9-engineering of HMC-1.2 cells renders a human mast cell line with a single D816V-KIT mutation: An improved preclinical model for research on mastocytosis
- PMID: 37025992
- PMCID: PMC10071028
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1078958
CRISPR/Cas9-engineering of HMC-1.2 cells renders a human mast cell line with a single D816V-KIT mutation: An improved preclinical model for research on mastocytosis
Abstract
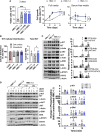
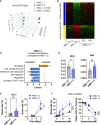
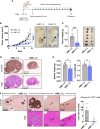
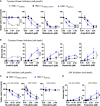
The HMC-1.2 human mast cell (huMC) line is often employed in the study of attributes of neoplastic huMCs as found in patients with mastocytosis and their sensitivity to interventional drugs in vitro and in vivo. HMC-1.2 cells express constitutively active KIT, an essential growth factor receptor for huMC survival and function, due to the presence of two oncogenic mutations (D816V and V560G). However, systemic mastocytosis is commonly associated with a single D816V-KIT mutation. The functional consequences of the coexisting KIT mutations in HMC-1.2 cells are unknown. We used CRISPR/Cas9-engineering to reverse the V560G mutation in HMC-1.2 cells, resulting in a subline (HMC-1.3) with a single mono-allelic D816V-KIT variant. Transcriptome analyses predicted reduced activity in pathways involved in survival, cell-to-cell adhesion, and neoplasia in HMC-1.3 compared to HMC-1.2 cells, with differences in expression of molecular components and cell surface markers. Consistently, subcutaneous inoculation of HMC-1.3 into mice produced significantly smaller tumors than HMC-1.2 cells, and in colony assays, HMC-1.3 formed less numerous and smaller colonies than HMC-1.2 cells. However, in liquid culture conditions, the growth of HMC-1.2 and HMC-1.3 cells was comparable. Phosphorylation levels of ERK1/2, AKT and STAT5, representing pathways associated with constitutive oncogenic KIT signaling, were also similar between HMC-1.2 and HMC-1.3 cells. Despite these similarities in liquid culture, survival of HMC-1.3 cells was diminished in response to various pharmacological inhibitors, including tyrosine kinase inhibitors used clinically for treatment of advanced systemic mastocytosis, and JAK2 and BCL2 inhibitors, making HMC-1.3 more susceptible to these drugs than HMC-1.2 cells. Our study thus reveals that the additional V560G-KIT oncogenic variant in HMC-1.2 cells modifies transcriptional programs induced by D816V-KIT, confers a survival advantage, alters sensitivity to interventional drugs, and increases the tumorigenicity, suggesting that engineered huMCs with a single D816V-KIT variant may represent an improved preclinical model for mastocytosis.
Keywords: D816V-KIT; HMC-1.2 cells; KIT variants; mast cell survival; mastocytosis; neoplastic human mast cells.
Copyright © 2023 Bandara, Falduto, Luker, Bai, Pfeiffer, Lack, Metcalfe and Olivera.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A new humanized in vivo model of KIT D816V+ advanced systemic mastocytosis monitored using a secreted luciferase.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):82985-83000. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12824. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27783996 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic growth-inhibitory effects of two tyrosine kinase inhibitors, dasatinib and PKC412, on neoplastic mast cells expressing the D816V-mutated oncogenic variant of KIT.Haematologica. 2007 Nov;92(11):1451-9. doi: 10.3324/haematol.11339. Haematologica. 2007. PMID: 18024392
-
Synergistic growth-inhibitory effects of ponatinib and midostaurin (PKC412) on neoplastic mast cells carrying KIT D816V.Haematologica. 2013 Sep;98(9):1450-7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2012.079202. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Haematologica. 2013. PMID: 23539538 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical human models and emerging therapeutics for advanced systemic mastocytosis.Haematologica. 2018 Nov;103(11):1760-1771. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.195867. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Haematologica. 2018. PMID: 29976735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Validation of KIT Inhibition in Advanced Systemic Mastocytosis.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2018 Oct;13(5):407-416. doi: 10.1007/s11899-018-0469-3. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2018. PMID: 30155614 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of the receptor KIT induces the secretion of exosome-like small extracellular vesicles.J Extracell Biol. 2024 Jan 23;3(1):e139. doi: 10.1002/jex2.139. eCollection 2024 Jan. J Extracell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38938682 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

