STAT3/NF‑κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides inhibit atherosclerosis through regulation of the STAT/NF‑κB signaling pathway in a mouse model of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 37026512
- PMCID: PMC10094942
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5240
STAT3/NF‑κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides inhibit atherosclerosis through regulation of the STAT/NF‑κB signaling pathway in a mouse model of atherosclerosis
Abstract
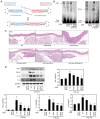
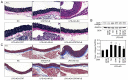
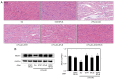
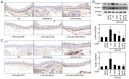
Atherosclerosis is a progressive chronic inflammatory condition that is the cause of most cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. The transcription factor nuclear factor‑κB (NF‑κB) regulates a number of genes involved in the inflammatory responses of cells that are critical to atherogenesis, and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3 is a key transcription factor in immunity and inflammation. Decoy oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) bind to sequence‑specific transcription factors and limit gene expression by interfering with transcription in vitro and in vivo. The present study aimed to investigate the beneficial functions of STAT3/NF‑κB decoy ODNs in liposaccharide (LPS)‑induced atherosclerosis in mice. Atherosclerotic injuries of mice were induced via intraperitoneal injection of LPS and the mice were fed an atherogenic diet. Ring‑type STAT3/NF‑κB decoy ODNs were designed and administered via an injection into the tail vein of the mice. To investigate the effect of STAT3/NF‑κB decoy ODNs, electrophoretic mobility shift assay, western blot analysis, histological analysis with hematoxylin and eosin staining, Verhoeff‑Van Gieson and Masson's trichrome staining were performed. The results revealed that STAT3/NF‑κB decoy ODNs were able to suppress the development of atherosclerosis by attenuating morphological changes and inflammation in atherosclerotic mice aortae, and by reducing pro‑inflammatory cytokine secretion through inhibition of the STAT3/NF‑κB pathway. In conclusion, the present study provided novel insights into the antiatherogenic molecular mechanism of STAT3/NF‑κB decoy ODNs, which may serve as an additional therapeutic intervention to combat atherosclerosis.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; decoy oligodeoxynucleotides; inflammation; nuclear factor‑κB; signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of chimeric decoy oligodeoxynucleotide in the regulation of transcription factors NF-κB and Sp1 in an animal model of atherosclerosis.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013 Apr;112(4):236-43. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.12029. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23107157
-
Exosome-mediated delivery of RBP-J decoy oligodeoxynucleotides ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in mice.Theranostics. 2022 Jan 24;12(4):1816-1828. doi: 10.7150/thno.69885. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35198075 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of STAT3 decoy oligodeoxynucleotides on human epithelial ovarian cancer cell growth in vivo.Int J Mol Med. 2013 Sep;32(3):623-8. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1431. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Int J Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23828376
-
Anti-oxidant gene therapy by NF kappa B decoy oligodeoxynucleotide.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2006 Apr;7(2):95-100. doi: 10.2174/138920106776597702. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16724943 Review.
-
Recent trends of NFκB decoy oligodeoxynucleotide-based nanotherapeutics in lung diseases.J Control Release. 2021 Sep 10;337:629-644. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.08.010. Epub 2021 Aug 8. J Control Release. 2021. PMID: 34375688 Review.
Cited by
-
Ginkgo Biloba Bioactive Phytochemicals against Age-Related Diseases: Evidence from a Stepwise, High-Throughput Research Platform.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 12;13(9):1104. doi: 10.3390/antiox13091104. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334763 Free PMC article.
-
The immune system in cardiovascular diseases: from basic mechanisms to therapeutic implications.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 May 23;10(1):166. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02220-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40404619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kahweol Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines in Tumor Necrosis Factor-α/Interferon-γ-Stimulated Human Keratinocyte HaCaT Cells.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Apr 18;46(4):3470-3483. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040218. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666948 Free PMC article.
-
A Positive Feedback Loop Between CXCL16 and the Inflammatory Factors IL-17A and TGF-β Promotes Large Artery Atherosclerosis by Activating the STAT3/NF-κB Pathway.Cardiovasc Ther. 2025 Mar 24;2025:2973633. doi: 10.1155/cdr/2973633. eCollection 2025. Cardiovasc Ther. 2025. PMID: 40165931 Free PMC article.
-
Amplified Production of a DNA Decoy Catalyzed by Intracellular MicroRNA.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 Apr 7;64(15):e202424421. doi: 10.1002/anie.202424421. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 39901657 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

