Compressive lesions of the head and neck: Common and uncommon must-know entities
- PMID: 37026517
- PMCID: PMC10973822
- DOI: 10.1177/19714009231166083
Compressive lesions of the head and neck: Common and uncommon must-know entities
Abstract
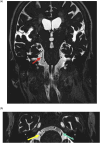
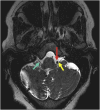
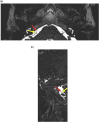
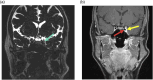
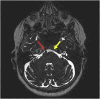
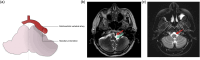
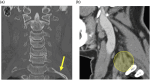
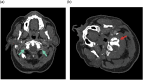
There are many lesions that cause compression of nerves and vessels in the head and neck, and they can often be overlooked in the absence of adequate history or if not suspected by the radiologist. Many of these lesions require a high index of suspicion and optimal positioning for imaging. While a multimodality approach is critical in the evaluation of compressive lesions, an MRI utilizing high-resolution (heavily weighted) T2-weighted sequence is extremely useful as a starting point. In this review, we aim to discuss the radiological features of the common and uncommon compressive lesions of the head and neck which are broadly categorized into vascular, osseous, and miscellaneous etiologies.
Keywords: cervical rib; compressive lesions; glossopharyngeal neuralgia; hemifacial spasm; optic neuropathy; trigeminal neuralgia; trochlear nerve palsy.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Concurrent trigeminal and glossopharyngeal neuralgia, hemifacial spasm and hypertension by neurovascular compression. Case report.J Neurosurg Sci. 1997 Sep;41(3):303-7. J Neurosurg Sci. 1997. PMID: 9444585
-
Hemifacial spasm associated with other cranial nerve syndromes: Literature review.Neurochirurgie. 2018 May;64(2):101-105. doi: 10.1016/j.neuchi.2018.01.002. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Neurochirurgie. 2018. PMID: 29680282 Review.
-
Imaging of Neurovascular Compression Syndromes: Trigeminal Neuralgia, Hemifacial Spasm, Vestibular Paroxysmia, and Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016 Aug;37(8):1384-92. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4683. Epub 2016 Feb 18. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016. PMID: 26892985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurovascular compression syndrome:Trigeminal neuralgia, hemifacial spasm, vestibular paroxysmia, glossopharyngeal neuralgia, four case reports and review of literature.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022 Oct;221:107401. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2022.107401. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 35932589 Review.
-
Multimodal Image-Based Virtual Reality Presurgical Simulation and Evaluation for Trigeminal Neuralgia and Hemifacial Spasm.World Neurosurg. 2018 May;113:e499-e507. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.02.069. Epub 2018 Feb 21. World Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 29476993
Cited by
-
Endovascular treatment for posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm with vertebral artery stenosis: The critical role of diagnosing osteophyte compression.Surg Neurol Int. 2024 Nov 15;15:421. doi: 10.25259/SNI_772_2024. eCollection 2024. Surg Neurol Int. 2024. PMID: 39640307 Free PMC article.
-
An Unusual Lingual Ulcerated Capillary Angioma After Dressmaker Needle Trauma, Above Migratory Glossitis Lesion, in a Patient With a History of Cancer: A Case Report.Case Rep Dent. 2025 May 6;2025:9921608. doi: 10.1155/crid/9921608. eCollection 2025. Case Rep Dent. 2025. PMID: 40365073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Melzack R, Terrence C, Fromm G, et al. Trigeminal neuralgia and atypical facial pain: use of the McGill pain questionnaire for discrimination and diagnosis. Pain 1986; 27: 297–302. - PubMed
-
- Olesen J. Headache classification committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders. Cephalalgia 2018: 38: 1–211. - PubMed
-
- De Ridder D, Sime MJ, Taylor P, et al. Microvascular decompression of the optic nerve for paroxysmal phosphenes and visual field deficit. World Neurosurg 2016; 85: 367.e5–367.e9. - PubMed
-
- Peker S, Kurtkaya Ö, Üzün I, et al. Microanatomy of the central myelin-peripheral myelin transition zone of the trigeminal nerve. Neurosurgery 2006; 59: 354–359; discussion 354-359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

