Emerging biologics for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 37026714
- PMCID: PMC10228297
- DOI: 10.1080/1061186X.2023.2199351
Emerging biologics for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
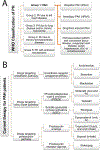
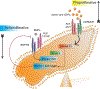
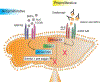
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a rare pulmonary vascular disorder, wherein mean systemic arterial pressure (mPAP) becomes abnormally high because of aberrant changes in various proliferative and inflammatory signalling pathways of pulmonary arterial cells. Currently used anti-PAH drugs chiefly target the vasodilatory and vasoconstrictive pathways. However, an imbalance between bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II (BMPRII) and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) pathways is also implicated in PAH predisposition and pathogenesis. Compared to currently used PAH drugs, various biologics have shown promise as PAH therapeutics that elicit their therapeutic actions akin to endogenous proteins. Biologics that have thus far been explored as PAH therapeutics include monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins, engineered cells, and nucleic acids. Because of their similarity with naturally occurring proteins and high binding affinity, biologics are more potent and effective and produce fewer side effects when compared with small molecule drugs. However, biologics also suffer from the limitations of producing immunogenic adverse effects. This review describes various emerging and promising biologics targeting the proliferative/apoptotic and vasodilatory pathways involved in PAH pathogenesis. Here, we have discussed sotatercept, a TGF-β ligand trap, which is reported to reverse vascular remodelling and reduce PVR with an improved 6-minute walk distance (6-MWDT). We also elaborated on other biologics including BMP9 ligand and anti-gremlin1 antibody, anti-OPG antibody, and getagozumab monoclonal antibody and cell-based therapies. Overall, recent literature suggests that biologics hold excellent promise as a safe and effective alternative to currently used PAH therapeutics.
Keywords: BMPRII; GDF; Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH); TGF-β; activin; biologics; ligand trap; monoclonal antibody; sotatercept.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bone morphogenetic protein signalling in pulmonary arterial hypertension: revisiting the BMPRII connection.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Jun 26;52(3):1515-1528. doi: 10.1042/BST20231547. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38716930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory Antibodies against Activin A and TGF-β Reduce Self-Supported, but Not Soluble Factors-Induced Growth of Human Pulmonary Arterial Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 28;19(10):2957. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102957. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30274147 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and TGF-β Superfamily Signaling: Focus on Sotatercept.BioDrugs. 2024 Nov;38(6):743-753. doi: 10.1007/s40259-024-00680-3. Epub 2024 Sep 18. BioDrugs. 2024. PMID: 39292393 Review.
-
TGFβ and BMPRII signalling pathways in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Drug Discov Today. 2019 Mar;24(3):703-716. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2018.12.001. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Drug Discov Today. 2019. PMID: 30529762 Review.
-
Impaired bone morphogenetic protein receptor II signaling in a transforming growth factor-β-dependent mouse model of pulmonary hypertension and in systemic sclerosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015 Mar 15;191(6):665-77. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201408-1464OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015. PMID: 25606692
Cited by
-
Endothelial Function in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: From Bench to Bedside.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 22;13(8):2444. doi: 10.3390/jcm13082444. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38673717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the Impact of miR-146a in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Pathophysiology and Right Ventricular Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 24;25(15):8054. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158054. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125620 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, function and drug discovery of GPCR signaling.Mol Biomed. 2023 Dec 4;4(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s43556-023-00156-w. Mol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 38047990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of different sequential triple oral combination therapies based selexipag on outcomes in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Clin Cardiol. 2024 Feb;47(2):e24245. doi: 10.1002/clc.24245. Clin Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38402556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper MM, et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2022. Aug 30. - PubMed
-
- Sommer N, Ghofrani HA, Pak O, et al. Current and future treatments of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Br J Pharmacol. 2021. Jan;178(1):6–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
