Toxoplasma ERK7 protects the apical complex from premature degradation
- PMID: 37027006
- PMCID: PMC10083718
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202209098
Toxoplasma ERK7 protects the apical complex from premature degradation
Abstract
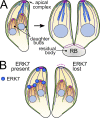
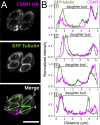
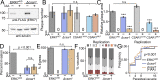
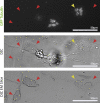
Accurate cellular replication balances the biogenesis and turnover of complex structures. In the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii, daughter cells form within an intact mother cell, creating additional challenges to ensuring fidelity of division. The apical complex is critical to parasite infectivity and consists of apical secretory organelles and specialized cytoskeletal structures. We previously identified the kinase ERK7 as required for maturation of the apical complex in Toxoplasma. Here, we define the Toxoplasma ERK7 interactome, including a putative E3 ligase, CSAR1. Genetic disruption of CSAR1 fully suppresses loss of the apical complex upon ERK7 knockdown. Furthermore, we show that CSAR1 is normally responsible for turnover of maternal cytoskeleton during cytokinesis, and that its aberrant function is driven by mislocalization from the parasite residual body to the apical complex. These data identify a protein homeostasis pathway critical for Toxoplasma replication and fitness and suggest an unappreciated role for the parasite residual body in compartmentalizing processes that threaten the fidelity of parasite development.
© 2023 O'Shaugnessy et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Revisiting the Role of Toxoplasma gondii ERK7 in the Maintenance and Stability of the Apical Complex.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0205721. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02057-21. Epub 2021 Oct 5. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34607461 Free PMC article.
-
Ancient MAPK ERK7 is regulated by an unusual inhibitory scaffold required for Toxoplasma apical complex biogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jun 2;117(22):12164-12173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1921245117. Epub 2020 May 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32409604 Free PMC article.
-
Multivalent Interactions Drive the Toxoplasma AC9:AC10:ERK7 Complex To Concentrate ERK7 in the Apical Cap.mBio. 2021 Feb 22;13(1):e0286421. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02864-21. Epub 2022 Feb 8. mBio. 2021. PMID: 35130732 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the tubulin-based cytoskeleton in the Toxoplasma gondii apical complex.Trends Parasitol. 2024 May;40(5):401-415. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2024.02.010. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Trends Parasitol. 2024. PMID: 38531711 Review.
-
Preparing for an invasion: charting the pathway of adhesion proteins to Toxoplasma micronemes.Parasitol Res. 2006 Apr;98(5):389-95. doi: 10.1007/s00436-005-0062-2. Epub 2005 Dec 30. Parasitol Res. 2006. PMID: 16385407 Review.
Cited by
-
Elucidating the spatio-temporal dynamics of the Plasmodium falciparum basal complex.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jun 3;20(6):e1012265. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012265. eCollection 2024 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38829893 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic approaches for protein kinase substrate identification in Apicomplexa.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2024 Sep;259:111633. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2024.111633. Epub 2024 May 29. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2024. PMID: 38821187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxoplasma gondii's Basal Complex: The Other Apicomplexan Business End Is Multifunctional.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Apr 29;12:882166. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.882166. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35573773 Free PMC article.
-
The initiation and early development of the tubulin-containing cytoskeleton in the human parasite Toxoplasma gondii.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Mar 1;35(3):ar37. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-11-0418. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38170577 Free PMC article.
-
Alveolin proteins in the Toxoplasma inner membrane complex form a highly interconnected structure that maintains parasite shape and replication.PLoS Biol. 2024 Sep 12;22(9):e3002809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002809. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 39264987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson-White, B.R., Ivey F.D., Cheng K., Szatanek T., Lorestani A., Beckers C.J., Ferguson D.J.P., Sahoo N., and Gubbels M.-J.. 2011. A family of intermediate filament-like proteins is sequentially assembled into the cytoskeleton of Toxoplasma gondii. Cell. Microbiol. 13:18–31. 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01514.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

