Neurons require glucose uptake and glycolysis in vivo
- PMID: 37027294
- PMCID: PMC10556202
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112335
Neurons require glucose uptake and glycolysis in vivo
Abstract
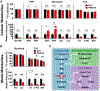
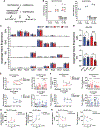
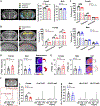
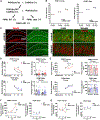
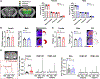
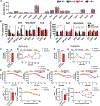
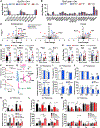
Neurons require large amounts of energy, but whether they can perform glycolysis or require glycolysis to maintain energy remains unclear. Using metabolomics, we show that human neurons do metabolize glucose through glycolysis and can rely on glycolysis to supply tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle metabolites. To investigate the requirement for glycolysis, we generated mice with postnatal deletion of either the dominant neuronal glucose transporter (GLUT3cKO) or the neuronal-enriched pyruvate kinase isoform (PKM1cKO) in CA1 and other hippocampal neurons. GLUT3cKO and PKM1cKO mice show age-dependent learning and memory deficits. Hyperpolarized magnetic resonance spectroscopic (MRS) imaging shows that female PKM1cKO mice have increased pyruvate-to-lactate conversion, whereas female GLUT3cKO mice have decreased conversion, body weight, and brain volume. GLUT3KO neurons also have decreased cytosolic glucose and ATP at nerve terminals, with spatial genomics and metabolomics revealing compensatory changes in mitochondrial bioenergetics and galactose metabolism. Therefore, neurons metabolize glucose through glycolysis in vivo and require glycolysis for normal function.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; bioenergetics; brain energy; galactose metabolism; glucose transporter; glycolysis; hyperpolarized magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging; metabolomics; neuronal glucose metabolism; pyruvate kinase.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.G.V.H. discloses that he is a scientific advisor for Agios Pharmaceuticals, iTeos Therapeutics, Sage Therapeutics, Faeth Therapeutics, DRIOA Ventures, and Auron Therapeutics. Y.H. discloses that he is a co-founder and scientific advisory board member of GABAeron.
Figures
References
-
- Patel AB, Lai JCK, Chowdhury GMI, Hyder F, Rothman DL, Shulman RG, and Behar KL (2014). Direct evidence for activity-dependent glucose phosphorylation in neurons with implications for the astrocyte-to-neuron lactate shuttle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 5385–5390. 10.1073/pnas.1403576111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ivanov AI, Malkov AE, Waseem T, Mukhtarov M, Buldakova S, Gubkina O, Zilberter M, and Zilberter Y (2014). Glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation in neurons and astrocytes during network activity in hippocampal slices. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab 34, 397–407. 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.222. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

