High-resolution structural information of membrane-bound α-synuclein provides insight into the MoA of the anti-Parkinson drug UCB0599
- PMID: 37027427
- PMCID: PMC10104497
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2201910120
High-resolution structural information of membrane-bound α-synuclein provides insight into the MoA of the anti-Parkinson drug UCB0599
Abstract
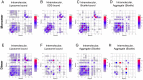
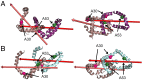
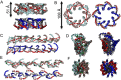
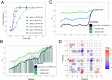
α-synuclein (αS) is an intrinsically disordered protein whose functional ambivalence and protein structural plasticity are iconic. Coordinated protein recruitment ensures proper vesicle dynamics at the synaptic cleft, while deregulated oligomerization on cellular membranes contributes to cell damage and Parkinson's disease (PD). Despite the protein's pathophysiological relevance, structural knowledge is limited. Here, we employ NMR spectroscopy and chemical cross-link mass spectrometry on 14N/15N-labeled αS mixtures to provide for the first time high-resolution structural information of the membrane-bound oligomeric state of αS and demonstrate that in this state, αS samples a surprisingly small conformational space. Interestingly, the study locates familial Parkinson's disease mutants at the interface between individual αS monomers and reveals different oligomerization processes depending on whether oligomerization occurs on the same membrane surface (cis) or between αS initially attached to different membrane particles (trans). The explanatory power of the obtained high-resolution structural model is used to help determine the mode-of-actionof UCB0599. Here, it is shown that the ligand changes the ensemble of membrane-bound structures, which helps to explain the success this compound, currently being tested in Parkinson's disease patients in a phase 2 trial, has had in animal models of PD.
Keywords: UCB0599; XL-MS; oligomeric structure; paramagnetic NMR spectroscopy; α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
T.S.B. and R.J.T. were employed by UCB Pharma and held stock options and shares of the same during the writing of this paper. T.C.S. and R.K. received funding from UCB Pharma and Neuropore Therapies. T.C.S., K.L., and R.K. are co-authors on a publication describing an early molecule showing a “proof-of mechanism” used by UCB0599.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Solid-state ¹³C NMR reveals annealing of raft-like membranes containing cholesterol by the intrinsically disordered protein α-Synuclein.J Mol Biol. 2013 Aug 23;425(16):2973-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.04.002. Epub 2013 Apr 11. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23583776 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein and biological membranes: the danger of loving too much.Chem Commun (Camb). 2023 Jul 13;59(57):8769-8778. doi: 10.1039/d3cc01682j. Chem Commun (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37345454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Ensembles of Membrane-bound α-Synuclein Reveal the Molecular Determinants of Synaptic Vesicle Affinity.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 8;6:27125. doi: 10.1038/srep27125. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27273030 Free PMC article.
-
Differential phospholipid binding of alpha-synuclein variants implicated in Parkinson's disease revealed by solution NMR spectroscopy.Biochemistry. 2010 Feb 9;49(5):862-71. doi: 10.1021/bi901723p. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20041693 Free PMC article.
-
Disruptive membrane interactions of alpha-synuclein aggregates.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019 May;1867(5):468-482. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019. PMID: 30315896 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation and Application of a PET Tracer in Preclinical and Phase 1 Studies to Determine the Brain Biodistribution of Minzasolmin (UCB0599).Mol Imaging Biol. 2024 Apr;26(2):310-321. doi: 10.1007/s11307-023-01878-7. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Mol Imaging Biol. 2024. PMID: 38110790 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Interplay between Copper, Phosphatidylserine, and α-Synuclein Suggests a Link between Copper Homeostasis and Synaptic Vesicle Cycling.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024 Aug 7;15(15):2884-2896. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00280. Epub 2024 Jul 16. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39013013 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of alpha-synuclein with membranes in Parkinson's disease: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.Neurobiol Dis. 2024 Oct 15;201:106646. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106646. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Neurobiol Dis. 2024. PMID: 39181187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matters arising: In vivo effects of the alpha-synuclein misfolding inhibitor minzasolmin supports clinical development in Parkinson's disease.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024 Mar 14;10(1):59. doi: 10.1038/s41531-024-00657-7. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024. PMID: 38486022 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Structures of Oligomeric States of Tau Protein, Amyloid-β, α-Synuclein and Prion Protein Implicated in Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease and Prionopathies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 4;25(23):13049. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313049. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684761 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alam P., Bousset L., Melki R., Otzen D. E., α-synuclein oligomers and fibrils: A spectrum of species, a spectrum of toxicities. J. Neurochem. 150, 522–534 (2019). - PubMed
-
- van Maarschalkerweerd A., Vetri V., Langkilde A. E., Fodera V., Vestergaard B., Protein/lipid coaggregates are formed during alpha-synuclein-induced disruption of lipid bilayers. Biomacromolecules 15, 3643–3654 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Weinreb P. H., Zhen W., Poon A. W., Conway K. A., Lansbury P. T. Jr., NACP, a protein implicated in Alzheimer’s disease and learning, is natively unfolded. Biochemistry 35, 13709–13715 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

