Induced pluripotent stem cell technology in bone biology
- PMID: 37028583
- PMCID: PMC10228209
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2023.116760
Induced pluripotent stem cell technology in bone biology
Abstract
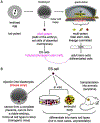
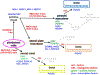
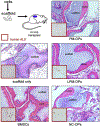
Technologies on the development and differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) are rapidly improving, and have been applied to create cell types relevant to the bone field. Differentiation protocols to form bona fide bone-forming cells from iPSCs are available, and can be used to probe details of differentiation and function in depth. When applied to iPSCs bearing disease-causing mutations, the pathogenetic mechanisms of diseases of the skeleton can be elucidated, along with the development of novel therapeutics. These cells can also be used for development of cell therapies for cell and tissue replacement.
Keywords: Induced pluripotent stem cells R; Models of disease; Osteogenic differentiation; Pluripotent stem cells; Reprogramming.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors have no conflicts of interest pertaining to the subject matter of this review.
Figures



References
-
- Hooke R, Micrographia: or some physiological descriptions of minute bodies made by magnifying glasses with observations and inquiries thereupon, Allestry J and Martyn J, London, 1665.
-
- Folkes M, Some account of Mr Leeuwenhoek’s curious microsopes lately presented to the Royal Society, Philosophical Transactions 32(380) (1723) 446–453.
-
- Schwann T, Schleiden MJ, Beiträge zur Phytogenesis, in: Muller J (Ed.), Archiv für Anatomie, Physiologie und wissenschaftliche Medicin, Eichler G, Berlin, 1838, pp. 137–176.
-
- Virchow R, Die Cellularpathologie in ihrer Begründung und in ihrer Auswirkung auf die physiologische und pathologische Gewebelehre, Hirschwald Verlag A., Berlin, 1858.
-
- Remak R, Untersuchungen uber die Entwickelung der Wirbelthiere, Reimer G, Berlin, 1855.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

