Exposure of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) to SARS-CoV-2 at predicted environmentally relevant concentrations: Outspreading warns about ecotoxicological risks to freshwater fish
- PMID: 37028679
- PMCID: PMC10076041
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163269
Exposure of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) to SARS-CoV-2 at predicted environmentally relevant concentrations: Outspreading warns about ecotoxicological risks to freshwater fish
Retraction in
-
Retraction notice to "Exposure of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) to SARS-CoV-2 at predicted environmentally relevant concentrations: Outspreading warns about ecotoxicological risks to freshwater fish" [Sci. Total Environ. 880 (2023) 163269].Sci Total Environ. 2025 Mar 1;967:178756. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2025.178756. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Sci Total Environ. 2025. PMID: 39952801 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
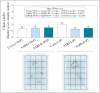
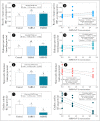
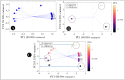
While the multifaceted social, economic, and public health impacts associated with the COVID-19 pandemic are known, little is known about its effects on non-target aquatic ecosystems and organisms. Thus, we aimed to evaluate the potential ecotoxicity of SARS-CoV-2 lysate protein (SARS.CoV2/SP02.2020.HIAE.Br) in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) at predicted environmentally relevant concentrations (0.742 and 2.226 pg/L), by 30 days. Although our data did not show locomotor alterations or anxiety-like or/and anxiolytic-like behavior, we noticed that exposure to SARS-CoV-2 negatively affected habituation memory and social aggregation of animals in response to a potential aquatic predator (Geophagus brasiliensis). An increased frequency of erythrocyte nuclear abnormalities was also observed in animals exposed to SARS-CoV-2. Furthermore, our data suggest that such changes were associated with a redox imbalance [↑ROS (reactive oxygen species), ↑H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide), ↓SOD (superoxide dismutase), and ↓CAT (catalase)], cholinesterasic effect [↑AChE (acetylcholinesterase) activity], as well as the induction of an inflammatory immune response [↑NO (nitric oxide), ↑IFN-γ (interferon-gamma), and ↓IL-10 (interleukin-10)]. For some biomarkers, we noticed that the response of the animals to the treatments was not concentration-dependent. However, principal component analysis (PCA) and the "Integrated Biomarker Response" index (IBRv2) indicated a more prominent ecotoxicity of SARS-CoV-2 at 2.226 pg/L. Therefore, our study advances knowledge about the ecotoxicological potential of SARS-CoV-2 and reinforces the presumption that the COVID-19 pandemic has negative implications beyond its economic, social, and public health impacts.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Danio rerio; Ecotoxicity; Environmental toxicology; New coronavirus.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest We confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this work, and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome. Furthermore, we ensure that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors and that there are no other persons who satisfied the criteria for authorship but are not listed. We further confirm that all have approved the order of authors listed in the manuscript of us. Due care has been taken to ensure the integrity of the work.
Figures






References
-
- Ahmad F., Richardson M.K. Exploratory behaviour in the open field test adapted for larval zebrafish: impact of environmental complexity. Behav. Process. 2013;92:88–98. - PubMed
-
- Alimba C.G., Bakare A.A. In vivo micronucleus test in the assessment of cytogenotoxicity of landfill leachates in three animal models from various ecological habitats. Ecotoxicology. 2016;25:310–319. - PubMed
-
- Almeida J.R., Oliveira C., Gravato C., Guilhermino L. Linking behavioural alterations with biomarkers responses in the european seabass Dicentrarchus labrax L. Exposed to the organophosphate pesticide fenitrothion. Ecotoxicology. 2010;19:1369–1381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

