EEG-LLAMAS: A low-latency neurofeedback platform for artifact reduction in EEG-fMRI
- PMID: 37028736
- PMCID: PMC10202030
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120092
EEG-LLAMAS: A low-latency neurofeedback platform for artifact reduction in EEG-fMRI
Abstract
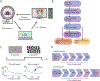
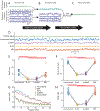
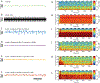
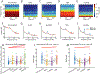
Simultaneous EEG-fMRI is a powerful multimodal technique for imaging the brain, but its use in neurofeedback experiments has been limited by EEG noise caused by the MRI environment. Neurofeedback studies typically require analysis of EEG in real time, but EEG acquired inside the scanner is heavily contaminated with ballistocardiogram (BCG) artifact, a high-amplitude artifact locked to the cardiac cycle. Although techniques for removing BCG artifacts do exist, they are either not suited to real-time, low-latency applications, such as neurofeedback, or have limited efficacy. We propose and validate a new open-source artifact removal software called EEG-LLAMAS (Low Latency Artifact Mitigation Acquisition Software), which adapts and advances existing artifact removal techniques for low-latency experiments. We first used simulations to validate LLAMAS in data with known ground truth. We found that LLAMAS performed better than the best publicly-available real-time BCG removal technique, optimal basis sets (OBS), in terms of its ability to recover EEG waveforms, power spectra, and slow wave phase. To determine whether LLAMAS would be effective in practice, we then used it to conduct real-time EEG-fMRI recordings in healthy adults, using a steady state visual evoked potential (SSVEP) task. We found that LLAMAS was able to recover the SSVEP in real time, and recovered the power spectra collected outside the scanner better than OBS. We also measured the latency of LLAMAS during live recordings, and found that it introduced a lag of less than 50 ms on average. The low latency of LLAMAS, coupled with its improved artifact reduction, can thus be effectively used for EEG-fMRI neurofeedback. A limitation of the method is its use of a reference layer, a piece of EEG equipment which is not commercially available, but can be assembled in-house. This platform enables closed-loop experiments which previously would have been prohibitively difficult, such as those that target short-duration EEG events, and is shared openly with the neuroscience community.
Keywords: Closed-loop; Denoising; Eeg-fmri; Real-time; Toolbox.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A real-time method to reduce ballistocardiogram artifacts from EEG during fMRI based on optimal basis sets (OBS).Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2016 Apr;127:114-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.01.018. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2016. PMID: 27000294
-
NeuXus open-source tool for real-time artifact reduction in simultaneous EEG-fMRI.Neuroimage. 2023 Oct 15;280:120353. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120353. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Neuroimage. 2023. PMID: 37652114
-
Ballistocardiogram artifact removal with a reference layer and standard EEG cap.J Neurosci Methods. 2014 Aug 15;233:137-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.06.021. Epub 2014 Jun 22. J Neurosci Methods. 2014. PMID: 24960423 Free PMC article.
-
Ballistocardiogram correction in simultaneous EEG/ fMRI recordings: a comparison of average artifact subtraction and optimal basis set methods using two popular software tools.Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2014;42(2):95-107. doi: 10.1615/critrevbiomedeng.2014011220. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2014. PMID: 25403874 Review.
-
Artifact Reduction in Simultaneous EEG-fMRI: A Systematic Review of Methods and Contemporary Usage.Front Neurol. 2021 Mar 11;12:622719. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.622719. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33776886 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CLET: Computation of Latencies in Event-related potential Triggers using photodiode on virtual reality apparatuses.Front Hum Neurosci. 2023 Sep 19;17:1223774. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1223774. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37795210 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study to assess synchronisation methods for combined simultaneous EEG and TMS acquisition.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 14;15(1):12816. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97225-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40229433 Free PMC article.
-
Test-retest reliability of EEG microstate metrics for evaluating noise reductions in simultaneous EEG-fMRI.Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024 Aug 29;2:imag-2-00272. doi: 10.1162/imag_a_00272. eCollection 2024. Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024. PMID: 40800321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abreu R, Jorge J, Figueiredo P, Mulert C, Lemieux L, 2022. EEG quality: the pulse artifact. In: EEG - FMRI: Physiological Basis, Technique, and Applications. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp. 167–188. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-07121-8_8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

