Robust, motion-free optical characterization of samples using actively-tunable Twyman-Green interferometry
- PMID: 37029205
- PMCID: PMC10082213
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-32791-2
Robust, motion-free optical characterization of samples using actively-tunable Twyman-Green interferometry
Abstract
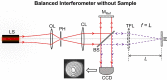
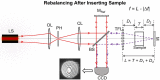
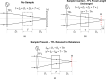
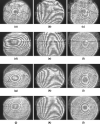
Optical interferometry-based techniques are ubiquitous in various measurement, imaging, calibration, metrological, and astronomical applications. Repeatability, simplicity, and reliability of measurements have ensured that interferometry in its various forms remains popular-and in fact continues to grow-in almost every branch of measurement science. In this paper, we propose a novel actively-controlled optical interferometer in the Twyman-Green configuration. The active beam control within the interferometer is a result of using an actively-controlled tunable focus lens in the sample arm of the interferometer. This innovation allows us to characterize transparent samples cut in the cubical geometry without the need for bulk mechanical motion within the interferometer. Unlike thickness/refractive index measurements with conventional Twyman-Green interferometers, the actively-tunable interferometer enables bulk-motion free thickness or refractive index sample measurements. With experimental demonstrations, we show excellent results for various samples that we characterized. The elimination of bulk motion from the measurement process promises to enable miniaturization of actively-tunable Twyman-Green interferometers for various applications.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
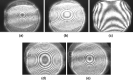
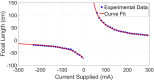
References
-
- Hariharan, P. Optical Interferometry 2nd edn. (Elsevier, 2003).
-
- Thompson, A. R., Moran, J. M. & Swenson, G. W. Interferometry and Synthesis in Radio Astronomy (Springer Nature, 2017).
-
- Harrison E, Hatt D, Prowse D, Wilbur-Ham J. A new interferometric manometer. Metrologia. 1976;12:115. doi: 10.1088/0026-1394/12/3/004. - DOI
-
- Riza NA, Sheikh M. Silicon carbide-based extreme environment hybrid design temperature sensor using optical pyrometry and laser interferometry. IEEE Sens. J. 2009;10:219–224. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2009.2031425. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

