Single cell transcriptomic analysis of HPV16-infected epithelium identifies a keratinocyte subpopulation implicated in cancer
- PMID: 37031202
- PMCID: PMC10082832
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-37377-0
Single cell transcriptomic analysis of HPV16-infected epithelium identifies a keratinocyte subpopulation implicated in cancer
Abstract
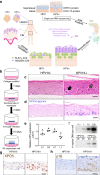
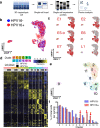
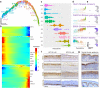
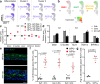
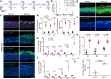
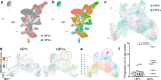
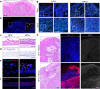
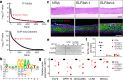
Persistent HPV16 infection is a major cause of the global cancer burden. The viral life cycle is dependent on the differentiation program of stratified squamous epithelium, but the landscape of keratinocyte subpopulations which support distinct phases of the viral life cycle has yet to be elucidated. Here, single cell RNA sequencing of HPV16 infected compared to uninfected organoids identifies twelve distinct keratinocyte populations, with a subset mapped to reconstruct their respective 3D geography in stratified squamous epithelium. Instead of conventional terminally differentiated cells, an HPV-reprogrammed keratinocyte subpopulation (HIDDEN cells) forms the surface compartment and requires overexpression of the ELF3/ESE-1 transcription factor. HIDDEN cells are detected throughout stages of human carcinogenesis including primary human cervical intraepithelial neoplasias and HPV positive head and neck cancers, and a possible role in promoting viral carcinogenesis is supported by TCGA analyses. Single cell transcriptome information on HPV-infected versus uninfected epithelium will enable broader studies of the role of individual keratinocyte subpopulations in tumor virus infection and cancer evolution.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R.L.F: Adagene Incorporated: Consulting; Aduro Biotech, Inc: Consulting, AstraZeneca/MedImmune: Clinical Trial, Research Funding; Bicara Therapeutics, Inc: Consultant; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Advisory Board, Clinical Trial, Research Funding; Brooklyn Immunotherapeutics LLC: Consultant; Catenion: Consultant; Coherus BioSciences, Inc.: Advisory Board; Eisai Europe Limited: Advisory Board; EMD Serono: Consultant; Everest Clinical Research Corporation: Consultant; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Consultant; Federation Bio, Inc: Consultant; Genocea Biosciences, Inc: Consultant; Genmab: Advisory Board; Hookipa Biotech GmbH: Advisory Board; Instil Bio, Inc: Advisory Board; Kowa Research Institute, Inc.: Consultant; Lifescience Dynamics Limited: Advisory Board; MacroGenics, Inc.: Advisory Board; MeiraGTx, LLC: Advisory Board; Merck: Advisory Board, Clinical Trial; Mirati Therapeutics, Inc: Consultant; Mirror Biologics Inc: Supplementary Data Safety Monitoring Board; Nanobiotix: Consultant; Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation: Consulting; Novasenta: Consulting, Stock, Research Funding; Numab Therapeutics AG: Advisory Board; OncoCyte Corporation: Advisory Board; Pfizer: Advisory Board; PPD Development, L.P.: Consultant; Rakuten Medical, Inc: Advisory Board; Sanofi: Consultant; Seagen, Inc: Advisory Board; SIRPant Immunotherapeutics, Inc: Advisory Board; Tesaro: Research Funding; Vir Biotechnology, Inc: Advisory Board; Zymeworks, Inc.: Consultant. T.J.H.: AstraZeneca, Caris, Clovis, Eisai, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Immunogen, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Mersana and Seagen (Advisory Boards). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

