Beyond an inflammatory mediator: Interleukin-1 in neurophysiology
- PMID: 37031383
- PMCID: PMC10988528
- DOI: 10.1113/EP090780
Beyond an inflammatory mediator: Interleukin-1 in neurophysiology
Abstract
New findings: What is the topic of this review? This review focuses on the physiological role of the cytokine interleukin-1β in the CNS. What advances does it highlight? Traditionally, interleukin-1β is known as a key mediator of inflammation and immunity. This review highlights the more recent findings describing how interleukin-1β signalling is required to maintain homeostasis in the CNS.
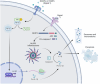
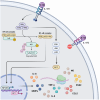
Abstract: Since its discovery in the early 1940s, the interleukin-1 (IL-1) cytokine family has been associated primarily with acute and chronic inflammation. The family member IL-1β is produced by different leucocytes, endothelial cells and epithelial cells. This cytokine has been characterized as a key modulator of inflammation and innate immunity because it induces the transcription of several downstream inflammatory genes. More recently, several groups have demonstrated that IL-1β production is also required to maintain homeostasis in several organ systems. This review focuses on providing an overview of the more recently characterized role of IL-1β in the physiology of the CNS. So far, IL-1β signalling has been implicated in neuronal survival, neurite growth, synaptic pruning, synaptic transmission, neuroplasticity and neuroendocrine functions.
Keywords: central nervous system; cytokine; inflammation; interleukin-1β; neurophysiology.
© 2023 The Authors. Experimental Physiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulation of interleukin-1beta mediated inflammatory response in human astrocytes by flavonoids: implications in neuroprotection.Brain Res Bull. 2007 Jun 15;73(1-3):55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2007.01.016. Epub 2007 Feb 28. Brain Res Bull. 2007. PMID: 17499637
-
Interleukin-1β suppression dampens inflammatory leucocyte production and uptake in atherosclerosis.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Oct 21;118(13):2778-2791. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab337. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 34718444 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Pro-Inflammatory and Regulatory Signaling by IL-33 in the Brain and Liver: A Focused Systematic Review of Mouse and Human Data and Risk of Bias Assessment of the Literature.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 30;21(11):3933. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113933. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32486265 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-33 and Behçet disease: Another cytokine among others.Hum Immunol. 2015 May;76(5):301-6. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2015.03.011. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Hum Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25814446 Review.
-
Long-term exposure to IL-1beta enhances Toll-IL-1 receptor-mediated inflammatory signaling in murine airway hyperresponsiveness.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2009 Sep;20(3):148-56. doi: 10.1684/ecn.2009.0156. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2009. PMID: 19825525
Cited by
-
T Cell Aging: An Important Target for Perioperative Immunomodulation.Clin Interv Aging. 2025 May 1;20:537-557. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S519438. eCollection 2025. Clin Interv Aging. 2025. PMID: 40330270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D Supplementation Is Associated with Inflammation Amelioration and Cognitive Improvement in Decompensated Patients with Cirrhosis.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 9;17(2):226. doi: 10.3390/nu17020226. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39861356 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between HLA Class II Gene Polymorphisms and Cytokine Levels in PLWH with HIV-Related Dermatoses in Latvia.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jun 15;61(6):1091. doi: 10.3390/medicina61061091. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40572779 Free PMC article.
-
Hypercholesterolemia Duration and Brain Area Determine Inflammatory Response Intensity and Apoptotic Mediator Activation in Apo E-/-/LDLR-/- Double-Knockout Mice.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 May 30;45(1):55. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01562-0. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40445431 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the study of mechanisms underlying olfactory dysfunction in obstructive sleep apnea:a narrative review.Sleep Biol Rhythms. 2025 Apr 3;23(3):263-274. doi: 10.1007/s41105-025-00582-z. eCollection 2025 Jul. Sleep Biol Rhythms. 2025. PMID: 40538384 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akama, K. T. , & Van Eldik, L. J. (2000). β‐amyloid stimulation of inducible nitric‐oxide synthase in astrocytes is interleukin‐1β‐ and tumor necrosis factor‐α (TNFα)‐dependent, and involves a TNFα receptor‐associated factor‐ and NFκB‐inducing kinase‐dependent signaling mechanism. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275(11), 7918–7924. - PubMed
-
- Atkins, E. (1984). Fever: The old and the new. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 149(3), 339–348. - PubMed
-
- Barbanel, G. , Ixart, G. , Szafarczyk, A. , Malaval, F. , & Assenmacher, I. (1990). Intrahypothalamic infusion of interleukin‐1 beta increases the release of corticotropin‐releasing hormone (CRH 41) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) in free‐moving rats bearing a push‐pull cannula in the median eminence. Brain Research, 516(1), 31–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

