Beyond an inflammatory mediator: Interleukin-1 in neurophysiology
- PMID: 37031383
- PMCID: PMC10988528
- DOI: 10.1113/EP090780
Beyond an inflammatory mediator: Interleukin-1 in neurophysiology
Abstract
New findings: What is the topic of this review? This review focuses on the physiological role of the cytokine interleukin-1β in the CNS. What advances does it highlight? Traditionally, interleukin-1β is known as a key mediator of inflammation and immunity. This review highlights the more recent findings describing how interleukin-1β signalling is required to maintain homeostasis in the CNS.
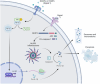
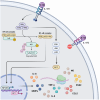
Abstract: Since its discovery in the early 1940s, the interleukin-1 (IL-1) cytokine family has been associated primarily with acute and chronic inflammation. The family member IL-1β is produced by different leucocytes, endothelial cells and epithelial cells. This cytokine has been characterized as a key modulator of inflammation and innate immunity because it induces the transcription of several downstream inflammatory genes. More recently, several groups have demonstrated that IL-1β production is also required to maintain homeostasis in several organ systems. This review focuses on providing an overview of the more recently characterized role of IL-1β in the physiology of the CNS. So far, IL-1β signalling has been implicated in neuronal survival, neurite growth, synaptic pruning, synaptic transmission, neuroplasticity and neuroendocrine functions.
Keywords: central nervous system; cytokine; inflammation; interleukin-1β; neurophysiology.
© 2023 The Authors. Experimental Physiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Akama, K. T. , & Van Eldik, L. J. (2000). β‐amyloid stimulation of inducible nitric‐oxide synthase in astrocytes is interleukin‐1β‐ and tumor necrosis factor‐α (TNFα)‐dependent, and involves a TNFα receptor‐associated factor‐ and NFκB‐inducing kinase‐dependent signaling mechanism. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275(11), 7918–7924. - PubMed
-
- Atkins, E. (1984). Fever: The old and the new. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 149(3), 339–348. - PubMed
-
- Barbanel, G. , Ixart, G. , Szafarczyk, A. , Malaval, F. , & Assenmacher, I. (1990). Intrahypothalamic infusion of interleukin‐1 beta increases the release of corticotropin‐releasing hormone (CRH 41) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) in free‐moving rats bearing a push‐pull cannula in the median eminence. Brain Research, 516(1), 31–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

