An integrated analysis of air pollution and meteorological conditions in Jakarta
- PMID: 37032334
- PMCID: PMC10083178
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-32817-9
An integrated analysis of air pollution and meteorological conditions in Jakarta
Abstract
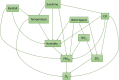
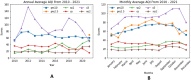
Air pollution and climate change are general problems for society. This paper proposes an integrated analysis of the Air Quality Index (AQI) and meteorological conditions in Jakarta. The column-based data integration model is applied to create integrated data of the Air Quality Index and meteorological conditions. The integrated data is then used to generate a causal graph using the PC algorithm. The causal graph reveals that there exist causal relationships between pollutants and meteorological conditions, e.g, humidity, rainfall, wind speed, and duration of sunshine affect particulate matter 10 (PM[Formula: see text]); wind speed affects sulfur dioxide (SO[Formula: see text]); temperature affects ozone (O[Formula: see text]). The historical data records that the average wind speed is decreased and the number of unhealthy days has risen. Ozone and particulate matter are two pollutants that mainly influence poor air quality in Jakarta. The integrated data is also used to train Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) for forecasting. Experimental results show that LSTM using integrated data produces smaller errors for forecasting AQI and meteorological conditions.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Kan H, Chen B, Zhao N, London SJ, Song G, Chen G, Zhang Y, Jiang L, Committee HHR. Part 1 a time-series study of ambient air pollution and daily mortality in Shanghai, China. Res. Rep. Health Eff. Inst. 2010;154(1):17–78. - PubMed
-
- Qian Z, He Q, Lin H-M, Kong L, Zhou D, Liang S, Zhu Z, Liao D, Liu W, Bentley CM, Dan J, Wang B, Yang N, Xu S, Gong J, Wei H, Sun H, Qin Z, Committee HHR. Part 2 association of daily mortality with ambient air pollution, and effect modification by extremely high temperature in Wuhan, China. Res. Rep. Health Eff. Inst. 2010;154(1):91–217. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

