Comparative analysis between STANDARD-E Covi-FERON ELISA with pre-existing IFN-γ release assays and determination of the optimum cutoff value for assessment of T-Cell response to SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 37032413
- PMCID: PMC10156097
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24882
Comparative analysis between STANDARD-E Covi-FERON ELISA with pre-existing IFN-γ release assays and determination of the optimum cutoff value for assessment of T-Cell response to SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Background: Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) release assays (IGRAs) are useful for the assessment of the T-cell response to severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). We aimed to assess the performance of the newly developed IGRA ELISA test compared to the pre-existing assays and to validate the cutoff value in real-world conditions.
Methods: We enrolled 219 participants and assessed agreement between STANDARD-E Covi-FERON ELISA with Quanti-FERON SARS-CoV-2 (QFN SARS-CoV-2), as well as with T SPOT Discovery SARS-CoV-2 based on Cohen's kappa-index. We further determined the optimal cutoff value for the Covi-FERON ELISA according to the immune response to vaccinations or infections.
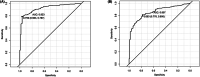
Results: We found a moderate agreement between Covi-FERON ELISA and QFN SARS-CoV-2 before vaccination (kappa-index = 0.71), whereas a weak agreement after the first (kappa-index = 0.40) and second vaccinations (kappa-index = 0.46). However, the analysis between Covi-FERON ELISA and T SPOT assay demonstrated a strong agreement (kappa-index >0.7). The cut-off value of the OS (original spike) marker was 0.759 IU/mL with a sensitivity of 96.3% and specificity of 78.7%, and that of the variant spike (VS) marker was 0.663 IU/mL with a sensitivity and specificity of 77.8% and 80.6%, respectively.
Conclusion: The newly determined cut-off value may provide an optimum value to minimize and prevent the occurrence of false-negative or false-positive during the assessment of T-cell immune response using Covi-FERON ELISA under real-world conditions.
Keywords: COVID-19; T-cell response; cutoff value; interferon-gamma; interferon-gamma release assay; kappa-index.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Performance of Interferon Gamma Release Assay (IGRA) for Cell-Mediated Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2.Clin Lab. 2023 Mar 1;69(3). doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2022.220643. Clin Lab. 2023. PMID: 36912314
-
Sustained cell-mediated but not humoral responses in rituximab-treated rheumatic patients after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 Feb 1;63(2):534-541. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead236. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 37228039 Free PMC article.
-
A Pilot Study for the Evaluation of an Interferon Gamma Release Assay (IGRA) To Measure T-Cell Immune Responses after SARS-CoV-2 Infection or Vaccination in a Unique Cloistered Cohort.J Clin Microbiol. 2022 Mar 16;60(3):e0219921. doi: 10.1128/jcm.02199-21. Epub 2022 Jan 12. J Clin Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35020419 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Performance of a Standardized Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Interferon-γ Release Assay for Simple Detection of T-Cell Responses After Infection or Vaccination.Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 24;75(1):e338-e346. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab1021. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34893816 Free PMC article.
-
[Evolution of IGRA researches].Kekkaku. 2008 Sep;83(9):641-52. Kekkaku. 2008. PMID: 18979999 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Longitudinal Comparison of Three T-Cell Assays and Three Antibody Assays Against SARS-CoV-2 Following Homologous mRNA-1273/mRNA-1273/mRNA-1273 and Heterologous ChAdOx1/ChAdOx1/BNT162b2 Vaccination: A Prospective Cohort in Naïve Healthcare Workers.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Nov 29;12(12):1350. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12121350. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39772013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Praet JT, Vandecasteele S, De Roo A, Vynck M, De Vriese AS, Reynders M. Dynamics of the cellular and humoral immune response after BNT162b2 mRNA Covid‐19 vaccination in Covid‐19 naive nursing home residents. J Infect Dis. 2021;224(10):1690‐1693. - PubMed
-
- Sahin U, Muik A, Derhovanessian E, et al. COVID‐19 vaccine BNT162b1 elicits human antibody and TH1 T‐cell responses. Nature. 2020;586(7830):594‐599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

