A Comprehensive Review on the Importance of MiRNA-206 in the Animal Model and Human Diseases
- PMID: 37032500
- PMCID: PMC10964108
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X21666230407124146
A Comprehensive Review on the Importance of MiRNA-206 in the Animal Model and Human Diseases
Abstract
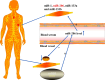
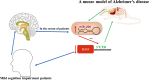
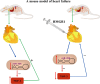
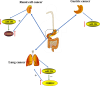
MicroRNA-206 (miR-206) is a microRNA that is involved in many human diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, osteoarthritis, depression, cancers, etc. Both inhibition effects and progression roles of miR-206 have been reported for the past few years. High expression of miR-206 was observed in patients with osteoarthritis, gastric cancer and epithelial ovarian cancer compared to normal people. The study also showed that miR-206 promotes cancer progression in breast cancer patients and avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Meanwhile, several studies have shown that expression levels of miR-206 were down-regulated in laryngeal carcinoma cell multiplication, as well as in hepatocellular carcinoma, non-small lung cancer and infantile hemangioma. Moreover, miR-206 was up-regulated in the mild stage of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients and then down-regulated in the moderate and severe stages, indicating that miR-206 has the double effects of starting and aggravating the disease. In neuropsychiatric disorders, such as depression, miR-206 also plays an important role in the progression of the disease; the level of miR-206 is most highly expressed in the brains of patients with depression. In the current review, we summarize the role of miR-206 in various diseases, and miR-206 may be developed as a new biomarker for diagnosing diseases in the near future.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease.; MiRNA; biomarkers; expression levels; human diseases; miR-206.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

