A Rare Case of Coccidioidomycosis Meningitis
- PMID: 37032742
- PMCID: PMC10079362
- DOI: 10.14740/jmc4040
A Rare Case of Coccidioidomycosis Meningitis
Abstract
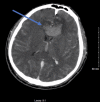
Disseminated coccidioidomycosis is a fungal disease endemic to the Southwest United States as well as South and Central America. This dimorphic fungus typically manifests as pulmonary infection; however, there are very rare instances of extrapulmonary disseminated disease especially in immunocompromised hosts. Here, we present a 46-year-old immunocompromised patient with a recent diagnosis of pulmonary coccidioidomycosis that initially presented with acute respiratory failure and was found to have coccidioidomycosis meningitis. This case highlights that despite early and adequate treatment of a known pulmonary coccidioidomycosis infection, dissemination of the disease can still ensue and should be considered in cases of acute encephalopathy.
Keywords: Coccidioidomycosis; Disseminated; Fungal infection; HIV; Immunocompromised.
Copyright 2023, Ghantarchyan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Akram SM, Koirala . StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): 2022. Coccidioidomycosis.
-
- Spickler AR. 2021. Retrieved from http://www.cfsph.iastate.edu/DiseaseInfo/factsheets.php.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
