Comparisons of the diagnostic accuracy across prostate health index, prostate health index density, and percentage free prostate-specific antigen for clinically significant prostate cancer: a prospective diagnostic study
- PMID: 37032752
- PMCID: PMC10080357
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-23-80
Comparisons of the diagnostic accuracy across prostate health index, prostate health index density, and percentage free prostate-specific antigen for clinically significant prostate cancer: a prospective diagnostic study
Abstract
Background: As the novel serum biomarkers, it has not been clearly clarified that the diagnostic accuracy of prostate health index (PHI) and prostate health index density (PHID) are superior to that of percentage free prostate-specific antigen (%fPSA) in detection of clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa), especially in the gray zone. Therefore, this study aimed to compare the diagnostic value of PHI, PHID, and %fPSA for csPCa in the patients with prostate-specific antigen (PSA) >4 ng/mL and those with PSA within 4-10 ng/mL.
Methods: In this study, the serum samples and clinicopathological features were prospectively obtained from the patients who underwent prostate biopsy between September 2019 and December 2020. According to the inclusion criteria, the patients with total PSA (tPSA) >4 ng/mL, prostate magnetic resonance imaging or ultrasound clearly suggesting an occupying lesion were enrolled in this study. The patients with Gleason score ≥7 indicated csPCa. The receiver operating characteristic curves and the area under the curve (AUC) values were used to assess the diagnostic performance.
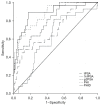
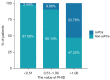
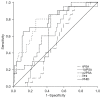
Results: Among the 296 patients (mean age 67.5 years, median tPSA 7.94 ng/mL) included in this study, there were 54 in the csPCa group (mean age 70.4 years, median tPSA 11.0 ng/mL) and 242 in the non-csPCa group (mean age 66.8 years, median tPSA 7.67 ng/mL). Based on the PSA level, there were 198 patients with PSA within the gray zone, which included 40 patients in the csPCa group and 158 in the non-csPCa group. In all patients, the sensitivity of PHID for detecting csPCa was 96.30%, and the specificity was 33.06% with the cut-off value of 0.51. Moreover, both PHID and PHI did better in the diagnosis of csPCa (AUC: 0.880 and 0.867, respectively) compared with other PSA derivative markers. Similarly, in the patients with PSA level in the gray zone, the diagnostic accuracy of PHID and PHI in predicting csPCa (AUC: 0.788 and 0.777, respectively) were better than other PSA derivative markers.
Conclusions: PHID presented the better diagnostic accuracy in predicting csPCa in patients with PSA in the gray zone than other PSA derivative markers, which could be a promising biomarker for making the biopsy strategy.
Keywords: Prostate cancer (PCa); gray zone; prostate health index (PHI); prostate health index density (PHID).
2023 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-23-80/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum (-2)proPSA/freePSAratio, (-2)proPSA/freePSA density, prostate health index, and prostate health index density as clues to reveal postoperative clinically significant prostate cancer in men with prostate-specific antigen 2-10 ng/mL.Prostate. 2024 Sep;84(12):1157-1164. doi: 10.1002/pros.24752. Epub 2024 May 26. Prostate. 2024. PMID: 38798011
-
Prostate Health Index Density Outperforms Prostate Health Index in Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Detection.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 19;11:772182. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.772182. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34869007 Free PMC article.
-
Modified Prostate Health Index Density Significantly Improves Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer (csPCa) Detection.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 7;12:864111. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.864111. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35463344 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical performance of serum [-2]proPSA derivatives, %p2PSA and PHI, in the detection and management of prostate cancer.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2014 Dec 25;2(4):343-50. eCollection 2014. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2014. PMID: 25606581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utility of PSA free-to-total ratio for clinically significant prostate cancer in men with a PSA level of <4 ng/mL.BJU Int. 2025 Apr;135(4):550-556. doi: 10.1111/bju.16597. Epub 2024 Nov 28. BJU Int. 2025. PMID: 39607059 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic value of prostate health index in patients with no index lesion on mpMRI or negative previous combined biopsy.Investig Clin Urol. 2025 Mar;66(2):124-129. doi: 10.4111/icu.20250007. Investig Clin Urol. 2025. PMID: 40047125 Free PMC article.
-
Technetium-99m-methylene diphosphonate single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography combined with prostate-specific antigen/free prostate-specific antigen ratio for bone metastasis of prostate cancer.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Jul 16;12(20):4082-4090. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i20.4082. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 39015893 Free PMC article.
-
The research progress on diagnostic indicators related to prostate-specific antigen gray-zone prostate cancer.BMC Cancer. 2025 Aug 4;25(1):1264. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14505-1. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40760471 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
