A novel loop-mediated isothermal amplification-lateral flow dipstick method for Helicobacter pylori detection
- PMID: 37032891
- PMCID: PMC10076779
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1094600
A novel loop-mediated isothermal amplification-lateral flow dipstick method for Helicobacter pylori detection
Abstract
Introduction: To eradicate Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) and reduce the risk of gastric cancer, a sensitive, specific, convenient, and simple detection method is needed. This study aimed to establish a novel loop-mediated isothermal amplification-lateral flow dipstick (LAMP-LFD) method for H. pylori detection.
Methods: LAMP primer design software was used to design primers for the conserved sites of the H. pylori ureB gene. UreB-FIP-labeled biotin was used for LAMP amplification, and FAM-labeled probes were specifically hybridized with LAMP amplification products, which were then detected by LFD. In addition, a clinical study was conducted to assess LAMP-LFD in 20 fecal samples.
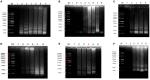
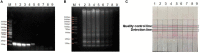
Results: The results of the optimization indicated that H. pylori could be specifically detected by LFD without cross-reaction with other non-H. pylori bacteria when the LAMP was performed at 65°C for 60 min. The lower limit of the detection method was 102 copies/μL, which was 100 times the sensitivity of polymerase chain reaction (PCR). H. pylori-positive fecal samples were detected by LAMP-LFD in 13/20 patients.
Discussion: In conclusion, a new LAMP-LFD assay has been fully established and confirmed for H. pylori detection. The entire process can be completed in approximately 1.5 h, with the advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, and simple operation. This study provides a novel potential method for the detection of H. pylori in the clinical settings of primary hospitals and low-resource countries.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; lateral flow dipstick; loop-mediated isothermal amplification; novel detection method; ureB gene.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Lu, Wang, Chen, Gao, Yin, Wu, Lv, Guo and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a chromatographic lateral-flow dipstick for rapid detection of Chattonella marina.Harmful Algae. 2019 Nov;89:101666. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2019.101666. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Harmful Algae. 2019. PMID: 31672231
-
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification-lateral-flow dipstick (LAMP-LFD) to detect Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Jan 30;35(2):31. doi: 10.1007/s11274-019-2601-5. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30701329 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a lateral flow dipstick test for the detection of 4 strains of Salmonella spp. in animal products and animal production environmental samples based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification.Anim Biosci. 2023 Apr;36(4):654-670. doi: 10.5713/ab.22.0151. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Anim Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36108678 Free PMC article.
-
Application of loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick to rapid and sensitive detection of Alexandrium catenella.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Feb;27(4):4246-4257. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06889-y. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31828710
-
Rapid and sensitive detection of shrimp yellow head virus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick.J Virol Methods. 2013 Mar;188(1-2):51-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2012.11.041. Epub 2012 Dec 7. J Virol Methods. 2013. PMID: 23219929 Review.
Cited by
-
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay coupled with lateral flow dipstick for the rapid detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius from dogs.Vet Res Commun. 2025 Jan 13;49(2):74. doi: 10.1007/s11259-024-10638-z. Vet Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 39804410
-
Recent advances in rapid detection of Helicobacter pylori by lateral flow assay.Arch Microbiol. 2025 Jan 16;207(2):35. doi: 10.1007/s00203-025-04239-w. Arch Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39820420 Review.
References
-
- Bakhtiari S., Alvandi A., Pajavand H., Navabi J., Najafi F., Abiri R., et al. . (2016). Development and diagnostic evaluation of loop-mediated isothermal amplification using a new gene target for rapid detection of Helicobacter pylori. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 9, e28831. 10.5812/jjm.28831 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Di Bonaventura G., Neri M., Angelucci D., Rosini S., Piccolomini M., Piccolomini R., et al. . (2004). Detection of Helicobacter Pylori by PCR on Gastric Biopsy Specimens Taken for CP Test: Comparison with Histopathological Analysis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 17, 77–82. 10.1177/039463200401700111 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

