The effect of mindfulness on social media addiction among Chinese college students: A serial mediation model
- PMID: 37032918
- PMCID: PMC10076863
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1087909
The effect of mindfulness on social media addiction among Chinese college students: A serial mediation model
Abstract
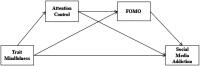
Introduction: The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated social media addiction (SMA), making it urgent to find effective interventions for social media addiction. Evidence has shown that mindfulness might be an effective intervention for social media addiction. However, psychological mechanisms by which mindfulness reduce social media use remain unclear. Here, we further addressed this issue to examine whether attentional control and fear of missing out (FOMO) mediate the relationship between mindfulness and SMA.
Methods: We recruited 446 college students from two universities in China and analyzed the data.
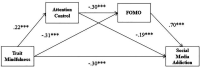
Results: The results suggest that there are mediation effects of attentional control and FOMO between mindfulness and SMA through 3 paths: path 1, mindfulness → attention control → SMA (-0.04); path 2, mindfulness → FOMO → SMA (-0.22); and path 3, mindfulness → attention control → FOMO → SMA (-0.05).
Discussion: Therefore, mindfulness-based interventions may be an effective way to alleviate social media addiction, especially mindfulness-based interventions targeting FOMO. At the end of the article, we also discussed the limitations of this study.
Keywords: attention control; college students; fear of missing out; mindfulness; social media addiction.
Copyright © 2023 Chang, Meng, Li, Liu, Yuan, Ni and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19-Related Post-Traumatic Stress Disorders Relation With Social Media Addiction Among University Students: Mediating Role of Fear of Missing Out.Psychiatry Investig. 2024 Sep;21(9):994-1006. doi: 10.30773/pi.2024.0112. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Psychiatry Investig. 2024. PMID: 39155551 Free PMC article.
-
Fear of Missing Out, Social Media Addiction, and Personality Traits Among Nursing Students: Cross-Sectional Study.JMIR Nurs. 2025 May 29;8:e71502. doi: 10.2196/71502. JMIR Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40440638 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring contributors to FoMO (fear of missing out) among university students: The role of social comparison, social media addiction, loneliness, and perfectionism.Acta Psychol (Amst). 2025 Mar;253:104771. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2025.104771. Epub 2025 Feb 3. Acta Psychol (Amst). 2025. PMID: 39904229
-
Influence of Mindfulness on Game Addiction-Mediating Role of Emotional Control.Psychol Rep. 2024 Feb 10:332941241232940. doi: 10.1177/00332941241232940. Online ahead of print. Psychol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38340087 Review.
-
The Emotional Reinforcement Mechanism of and Phased Intervention Strategies for Social Media Addiction.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 May 13;15(5):665. doi: 10.3390/bs15050665. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40426443 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of brief online mindfulness-based intervention on different types of mobile phone addiction: mechanisms of influence of trait mindfulness.Front Psychol. 2025 Feb 17;16:1400327. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1400327. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40034944 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of multidimensional excessive social media use on academic performance: the moderating role of mindfulness.Front Psychol. 2025 Jun 23;16:1579509. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1579509. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40625430 Free PMC article.
-
A Multi- Mediation Analysis on the Impact of Social Media and Internet Addiction on University and High School Students' Mental Health Through Social Capital and Mindfulness.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 Jan 2;22(1):57. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22010057. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39857510 Free PMC article.
-
Mindfulness-Based Intervention in Schools: Addressing Social Media Burnout and Enhancing Well-Being in Adolescents.Children (Basel). 2025 Jun 23;12(7):826. doi: 10.3390/children12070826. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723019 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of academic anxiety on smartphone addiction among college students: the mediating role of self-regulatory fatigue and the moderating role of mindfulness.BMC Psychol. 2025 Apr 9;13(1):354. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-02696-y. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40205575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iwamoto D, Chun H. The emotional impact of social media in higher education. Int J High Educ. (2020) 9:239–47. doi: 10.5430/ijhe.v9n2p239 - DOI
-
- Siste K, Hanafi E, Sen L, Christian H, Adrian Siswidiani LP, Limawan AP, et al. . The impact of physical distancing and associated factors towards internet addiction among adults in Indonesia during COVID-19 pandemic: a nationwide web-based study. Front Psych. (2020) 11:580977. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.580977, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

