Social support and quality of life in migrant workers: Focusing on the mediating effect of healthy lifestyle
- PMID: 37033034
- PMCID: PMC10076876
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1061579
Social support and quality of life in migrant workers: Focusing on the mediating effect of healthy lifestyle
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the relationship between social support and quality of life of Chinese migrant workers and to explore the mediating role of healthy lifestyles in social support and quality of life.
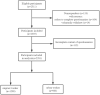
Methods: Using a stratified multi-stage sampling method, 1, 298 migrant workers and 983 urban workers across 110 neighborhood committees in five economic development zones in eastern China were surveyed. The social support level of participants was quantified using the Social Support Rating Scale, and quality of life was evaluated using the SF-8. Healthy lifestyle was evaluated based on a combination of sleep, smoking, alcohol consumption, and exercise. Multiple linear regression analysis was used to assess the relationship between quality of life and social support. Stepwise regression was used to analyze the mediating effect of healthy lifestyle, social support, and quality of life among migrant workers.
Results: Total SSRS and total SF-8 scores of migrant workers were significantly higher than those of urban workers (P < 0.001). After controlling for confounders, social support showed an independent positive association with quality of life for both migrant (β = 0.50, P < 0.05) and urban workers (β = 0.62, P < 0.05). Mediation effect analysis revealed that healthy lifestyle partially mediated the relation between social support and quality of life of migrant workers with a mediation effect of 0.07, accounting for 11.70% of the total effect.
Conclusions: This study showed a significant correlation between social support and quality of life of Chinese migrant workers, with healthy lifestyle playing a mediating role. Improving the social support and health literacy of migrant workers and developing a healthy lifestyle are key to improving their quality of life.
Keywords: lifestyle; mediating effect; migrant worker; quality of life; social support.
Copyright © 2023 Yang, Zhao, Lin, Qian, Zhang and Cai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relationship between social support and depressive symptoms among internal migrant workers and the mediating role of healthy lifestyle: a cross-sectional study in China.BMJ Open. 2025 Jan 6;15(1):e089486. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-089486. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39762093 Free PMC article.
-
The chain mediation model of social support and life satisfaction among migrant older adults with children: The role of mental health and sleep quality.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2023 Dec;115:105122. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2023.105122. Epub 2023 Jul 8. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2023. PMID: 37441894
-
Influence of Social Support on Health-Related Quality of Life in New-Generation Migrant Workers in Eastern China.Iran J Public Health. 2013 Aug;42(8):806-12. Iran J Public Health. 2013. PMID: 26056633 Free PMC article.
-
Health-related quality of life of migrant workers: a systematic literature review.BMC Public Health. 2023 May 30;23(1):1004. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15981-5. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37254085 Free PMC article.
-
LIFESTYLE AND QUALITY OF LIFE.In: Taher AT, Farmakis D, Porter JB, Cappellini MD, Musallam KM, editors. Guidelines for the Management of Transfusion-Dependent β-Thalassaemia (TDT) [Internet]. 5th edition. Nicosia, Cyprus: Thalassaemia International Federation; 2025. Chapter 11. In: Taher AT, Farmakis D, Porter JB, Cappellini MD, Musallam KM, editors. Guidelines for the Management of Transfusion-Dependent β-Thalassaemia (TDT) [Internet]. 5th edition. Nicosia, Cyprus: Thalassaemia International Federation; 2025. Chapter 11. PMID: 40367257 Free Books & Documents. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The mediating role of social support in self-management and quality of life in patients with liver cirrhosis.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 8;15(1):4758. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81943-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39922844 Free PMC article.
-
Health inequality of rural-to-urban migrant workers in eastern China and its decomposition: a comparative cross-sectional study.Front Public Health. 2024 May 13;12:1365241. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1365241. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38803809 Free PMC article.
-
The public health consequences of mandatory return migration: a call for action.Front Public Health. 2025 Apr 30;13:1577018. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1577018. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40371303 Free PMC article.
-
The Mediating Role of Posttraumatic Stress Symptoms in the Relationship between Adult Attachment and Quality of Life.Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2024 Oct 7;14(10):2735-2753. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe14100180. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2024. PMID: 39452175 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Social Dynamics on Biological Aging and the Health of Historically Marginalized Populations: A Biopsychosocial Model for Health Disparities.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Apr 26;21(5):554. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21050554. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38791769 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- China NBoSo . Statistical Report on National Economy Social Development of People's Republic of China in 2021. Beijing: National Bureau of Statistics of China (2022). Available online at: http://www.stats.gov.cn/xxgk/sjfb/zxfb2020/202202/t20220228_1827971.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

