Humoral response after a fourth dose of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in immunocompromised patients. Results of a systematic review
- PMID: 37033069
- PMCID: PMC10076800
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1108546
Humoral response after a fourth dose of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in immunocompromised patients. Results of a systematic review
Abstract
Background and objective: The fourth dose the COVID-19 vaccine was first proposed to immunocompromised patients. The aim of the article is to systematically review the literature and report the humoral response and outcomes after the fourth dose administration in people with impaired immune system.
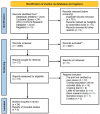
Methods: Published studies on the humoral response, efficacy and safety of the fourth dose of the COVID-19 vaccine were analyzed in various settings of immunocompromised patients. We conducted systematic searches of PubMed, Cochrane Library and WHO COVID-19 Research Database for series published through January 31, 2023, using the search terms "fourth dose" or "second booster" or "4th dose" and "Coronavirus" or "COVID-19" or "SARS-CoV-2." All articles were selected according to the PRISMA guidelines.
Results: A total of 24 articles including 2,838 patients were comprised in the systematic review. All the studies involved immunocompromised patients, including solid organ transplant recipients, patients with autoimmune rheumatic disease, patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and patients with blood cancers or diseases. Almost all patients received BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 as fourth dose. All the studies demonstrated the increase of antibody titers after the fourth dose, both in patients who had a serological strong response and in those who had a weak response after the third dose. No serious adverse events after the 4th dose have been reported by 13 studies. COVID-19 infection after the fourth dose ranged from 0 to 21%.
Conclusion: The present review highlights the importance of the fourth dose of covid-19 vaccines for immunocompromised patients. Across the included studies, a fourth dose was associated with improved seroconversion and antibody titer levels. In particular, a fourth dose was associated with increasing immunogenicity in organ transplant recipients and patients with hematological cancers, with a very low rate of serious side effects.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; fourth dose; immune system; immunocompromised; second booster.
Copyright © 2023 Martinelli, Pascucci and Laurenti.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of covid-19 vaccines in immunocompromised patients: systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ. 2022 Mar 2;376:e068632. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2021-068632. BMJ. 2022. PMID: 35236664 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and safety of a booster dose of a self-amplifying RNA COVID-19 vaccine (ARCT-154) versus BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine: a double-blind, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3, non-inferiority trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2024 Apr;24(4):351-360. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00650-3. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38141632 Clinical Trial.
-
Study of efficacy and longevity of immune response to third and fourth doses of COVID-19 vaccines in patients with cancer: A single arm clinical trial.Elife. 2023 Mar 28;12:e83694. doi: 10.7554/eLife.83694. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36975207 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prospective Evaluation of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Vaccine Responses Across a Broad Spectrum of Immunocompromising Conditions: the COVID-19 Vaccination in the Immunocompromised Study (COVICS).Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 24;75(1):e630-e644. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac103. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35179197 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and Risk Factors Associated With Poor Humoral Immune Response of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Recipients of Solid Organ Transplant: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Apr 1;5(4):e226822. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.6822. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 35412626 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lipid Metabolism Modulation during SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Spotlight on Extracellular Vesicles and Therapeutic Prospects.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 4;25(1):640. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010640. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutralizing activity of a third dose of CoronaVac against Omicron subvariants within a 20-month follow-up study.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Aug 1;19(2):2242217. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2242217. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37529941 Free PMC article.
-
Immunocytometric analysis of patients with thymic epithelial tumors revealed that COVID-19 vaccine booster strongly enhanced the immune response.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 29;14:1233056. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1233056. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37705978 Free PMC article.
-
Humoral responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in vasculitis-related immune suppression.Sci Adv. 2025 Feb 14;11(7):eadq3342. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adq3342. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 39937891 Free PMC article.
-
Multimorbidity and Serological Response to SARS-CoV-2 Nine Months after 1st Vaccine Dose: European Cohort of Healthcare Workers-Orchestra Project.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Aug 8;11(8):1340. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11081340. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) vaccinations . Geneva: World Health Organization. Available online at: https://covid19.who.int/data
-
- COVID-19 Vaccinations in the United States . Center for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Available online at: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccinations_vacc-total-admin-...
-
- ECDC and EMA update recommendations on additional booster doses of COVID-19 vaccines . Amsterdam: European Medicines Agency. Available online at: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/news-events/ecdc-and-ema-update-recommenda... (accessed Oct 23, 2022).
-
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA . Authorizes Second Booster Dose of Two COVID-19 Vaccines for Older and Immunocompromised Individuals. Silver Spring: U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous