Type A Aortic Dissection with Antegrade Intimointimal Intussusception
- PMID: 37033107
- PMCID: PMC10077976
- DOI: 10.14797/mdcvj.1210
Type A Aortic Dissection with Antegrade Intimointimal Intussusception
Abstract
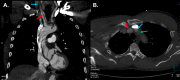
We describe a 60-year-old man with a history of hypertension who presented to an outside emergency department with chest pain and left lower extremity numbness and weakness. Computed tomography (CT) revealed Stanford type A aortic dissection (TAAD), and he was transferred to our institution for emergent open surgical repair. Review of the outside CT showed no dissection flap in the ascending aorta and a complex flap in the proximal descending thoracic aorta consistent with complex intimal transection at the sinotubular junction and intimointimal intussusception. This case presents high-resolution diagnostic and intraoperative images and illustrates the importance of rapid diagnosis and recognition of the potentially complex nature of the aortic dissection to avoid impending hemodynamic deterioration.
Keywords: intimointimal intussusception; type A aortic dissection.
Copyright: © 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Michael J. Reardon, MD, is a consultant for Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Gore Medical. The other authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Levy D, Goyal A, Grigorova Y, et al. Aortic Dissection. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Jan. PMID: 28722992 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

