Effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the liver
- PMID: 37033147
- PMCID: PMC10075054
- DOI: 10.5501/wjv.v12.i2.109
Effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the liver
Abstract
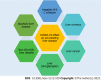
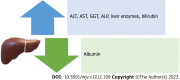
There have been numerous concerns about the disease and how it affects the human body since the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic began in December 2019. The impact of SARS-CoV-2 on the liver is being carefully investigated due to an increase in individuals with hepatitis and other liver illnesses, such as alcoholic liver disease. Additionally, the liver is involved in the metabolism of numerous drugs used to treat comorbidities and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Determining how SARS-CoV-2 affects the liver and what factors place individuals with COVID-19 at a higher risk of developing liver problems are the two main objectives of this study. This evaluation of the literature included research from three major scientific databases. To provide an update on the current impact of COVID-19 on the liver, data was collected and relevant information was incorporated into the review. With more knowledge about the effect of the disease on the liver, better management and therapeutics can be developed, and education can ultimately save lives and reduce the long-term impact of the pandemic on our population.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Hepatic complications; Liver; SARS-CoV-2.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

References
-
- McIntosh K, Hirsch MS, Bloom A. COVID-19: Epidemiology, virology, and prevention. 16 May 2022. UpToDate. [cited 12 June 2022]. In: UpToDate.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

