Identifying novel selective PPO inhibitors through structure-based virtual screening and bio-evaluation
- PMID: 37033434
- PMCID: PMC10075065
- DOI: 10.1039/d2ra08006k
Identifying novel selective PPO inhibitors through structure-based virtual screening and bio-evaluation
Abstract
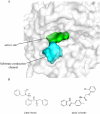
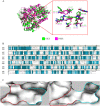
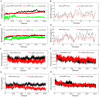
Protoporphyrinogen oxidase (PPO) is a key enzyme in chlorophyll and heme biosynthesis, and the development of its inhibitors is of great importance both in the pharmaceutical and pesticide industries. However, the currently developed PPO inhibitors have insignificant bio-selectivity and have a serious impact on non-target organisms. In this study, a docking-based virtual screening approach combined with bio-activity testing was used to obtain novel selective inhibitors of PPO. The results of the bio-activity test showed that thirteen compounds showed 10-fold selectivity over human PPO. And the best selective compound, ZINC70338, has a K i value of 2.21 μM for Nicotiana tabacum PPO and >113-fold selectivity for human PPO. The selectivity mechanism of ZINC70338 in different species of PPO was then analyzed by molecular dynamics simulations to provide a design basis and theoretical guidance for the design of novel selective inhibitors.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Hao G. F. Zuo Y. Yang S. G. et al., Protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitor: an ideal target for herbicide discovery. Chimia. 2011;65(12):961–969. - PubMed
-
- Gunshin H. Mackenzie B. Berger U. V. et al., Cloning and characterization of a mammalian proton-coupled metal-ion transporter. Nature. 1997;388(6641):482–488. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

