Anti-viral drug discovery against monkeypox and smallpox infection by natural curcumin derivatives: A Computational drug design approach
- PMID: 37033493
- PMCID: PMC10073709
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1157627
Anti-viral drug discovery against monkeypox and smallpox infection by natural curcumin derivatives: A Computational drug design approach
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Anti-viral drug discovery against monkeypox and smallpox infection by natural curcumin derivatives: a computational drug design approach.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jun 9;13:1217334. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1217334. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37360525 Free PMC article.
Abstract
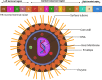
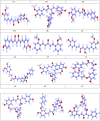
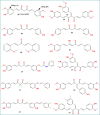
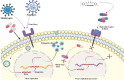
Background: In the last couple of years, viral infections have been leading the globe, considered one of the most widespread and extremely damaging health problems and one of the leading causes of mortality in the modern period. Although several viral infections are discovered, such as SARS CoV-2, Langya Henipavirus, there have only been a limited number of discoveries of possible antiviral drug, and vaccine that have even received authorization for the protection of human health. Recently, another virial infection is infecting worldwide (Monkeypox, and Smallpox), which concerns pharmacists, biochemists, doctors, and healthcare providers about another epidemic. Also, currently no specific treatment is available against Monkeypox. This research gap encouraged us to develop a new molecule to fight against monkeypox and smallpox disease. So, firstly, fifty different curcumin derivatives were collected from natural sources, which are available in the PubChem database, to determine antiviral capabilities against Monkeypox and Smallpox.
Material and method: Preliminarily, the molecular docking experiment of fifty different curcumin derivatives were conducted, and the majority of the substances produced the expected binding affinities. Then, twelve curcumin derivatives were picked up for further analysis based on the maximum docking score. After that, the density functional theory (DFT) was used to determine chemical characterizations such as the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO), lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO), softness, and hardness, etc.
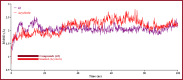
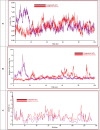
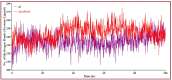
Results: The mentioned derivatives demonstrated docking scores greater than 6.80 kcal/mol, and the most significant binding affinity was at -8.90 kcal/mol, even though 12 molecules had higher binding scores (-8.00 kcal/mol to -8.9 kcal/mol), and better than the standard medications. The molecular dynamic simulation is described by root mean square deviation (RMSD) and root-mean-square fluctuation (RMSF), demonstrating that all the compounds might be stable in the physiological system.
Conclusion: In conclusion, each derivative of curcumin has outstanding absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) characteristics. Hence, we recommended the aforementioned curcumin derivatives as potential antiviral agents for the treatment of Monkeypox and Smallpox virus, and more in vivo investigations are warranted to substantiate our findings.
Keywords: DFT; admet; curcumin; molecular docking; molecular dynamic simulation; monkeypox; smallpox virus.
Copyright © 2023 Akash, Hossain, Hossain, Rahman, Ahmed, Ali, Valis, Kuca and Sharma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Screening of potential inhibitors against structural proteins from Monkeypox and related viruses of Poxviridae family via docking and molecular dynamics simulation.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024;42(20):10978-10993. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2259489. Epub 2023 Sep 29. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37776002
-
Investigation of the New Inhibitors by Sulfadiazine and Modified Derivatives of α-D-glucopyranoside for White Spot Syndrome Virus Disease of Shrimp by In Silico: Quantum Calculations, Molecular Docking, ADMET and Molecular Dynamics Study.Molecules. 2022 Jun 8;27(12):3694. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123694. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744817 Free PMC article.
-
A drug design strategy based on molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations applied to development of inhibitor against triple-negative breast cancer by Scutellarein derivatives.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 12;18(10):e0283271. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283271. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37824496 Free PMC article.
-
Smallpox and monkeypox: Looking back and looking ahead.Cleve Clin J Med. 2023 Mar 1;90(3):141-144. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.90a.22067. Cleve Clin J Med. 2023. PMID: 36858615 Review.
-
A review on computational studies and bioinformatics analysis of potential drugs against monkeypox virus.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Aug;42(12):6091-6107. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2231542. Epub 2023 Jul 4. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37403283 Review.
Cited by
-
Advancements in Dermatological Applications of Curcumin: Clinical Efficacy and Mechanistic Insights in the Management of Skin Disorders.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024 May 13;17:1083-1092. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S467442. eCollection 2024. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38765192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-based drug designing for potential antiviral activity of selected natural product against Monkeypox (Mpox) virus and its host targets.Virusdisease. 2024 Dec;35(4):589-608. doi: 10.1007/s13337-024-00900-y. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Virusdisease. 2024. PMID: 39677842
-
Pharmacological treatment and vaccines in monkeypox virus: a narrative review and bibliometric analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 5;14:1149909. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1149909. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37214444 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akash S. (2002). Computational screening of novel therapeutic and potent molecules from bioactive trehalose and it’s eight derivatives by different insilico studies for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Organic Communications 15, 1–10. doi: 10.25135/acg.oc.134.2204.2446 - DOI
-
- Akash S., Kumar A., Rahman M., Emran T. B., Sharma R., Singla R. K., et al. (2022. a). Development of new bioactive molecules to treat breast and lung cancer with natural myricetin and its derivatives: A computational and SAR approach. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12, 1400. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.952297 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akash S., Rahman M. M., Islam M. R., Sharma R. (2022. b). Emerging global concern of langya henipavirus: Pathogenicity, virulence, genomic features, and future perspectives. J. Med. Virol, 1–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

