Extraventricular Neurocytoma of the Posterior Fossa: A Case Report Written by ChatGPT
- PMID: 37033498
- PMCID: PMC10076908
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.35850
Extraventricular Neurocytoma of the Posterior Fossa: A Case Report Written by ChatGPT
Abstract
ChatGPT (Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer) is the latest artificial intelligence (AI) tool that has taken the internet by storm. A large language model-based AI tool, ChatGPT is used to generate natural prose-like answers learning from a large database of text. A lot is being written and spoken about the future of academic writing using this tool.We attempt to generate a short case report of a brain tumour labelled extraventriuclar neurocytoma (EVN) which is a rare tumour of the central nervous system. When posed with a set of questions on this uncommon topic, ChatGPT did well with relevant but not very specific answers. Validation of the information is an issue like with most machine learning solutions. This case report is an attempt to summarise EVN and its management. Q: Summarise extraventricular neurocytoma. ChatGPT: EVN is a rare and benign tumor that typically occurs in the brain. It often causes no symptoms, but as it grows, it can cause headaches, seizures, and changes in vision or balance. Surgery is usually curative, but there is a lack of studies to know the best treatment options. The prognosis is generally good with high rates of long-term survival and low rates of recurrence. Text italicised in the article is generated by ChatGPT.
Keywords: artificial intelligence (ai); brain tumour; chatgpt; extraventricular neurocytoma; neuro oncology.
Copyright © 2023, Hegde et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
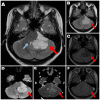
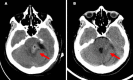


Similar articles
-
Ectopic Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumor: A Case Report Written With the Help of ChatGPT.Cureus. 2023 Oct 13;15(10):e46999. doi: 10.7759/cureus.46999. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37965416 Free PMC article.
-
From human writing to artificial intelligence generated text: examining the prospects and potential threats of ChatGPT in academic writing.Biol Sport. 2023 Apr;40(2):615-622. doi: 10.5114/biolsport.2023.125623. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Biol Sport. 2023. PMID: 37077800 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of ChatGPT-generated articles with human-written articles.Skeletal Radiol. 2023 Sep;52(9):1755-1758. doi: 10.1007/s00256-023-04340-5. Epub 2023 Apr 14. Skeletal Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37059827
-
Utilizing ChatGPT in clinical research related to anesthesiology: a comprehensive review of opportunities and limitations.Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2023 Jul;18(3):244-251. doi: 10.17085/apm.23056. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2023. PMID: 37691594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ChatGPT in medicine: an overview of its applications, advantages, limitations, future prospects, and ethical considerations.Front Artif Intell. 2023 May 4;6:1169595. doi: 10.3389/frai.2023.1169595. eCollection 2023. Front Artif Intell. 2023. PMID: 37215063 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of an AI-Generated Case Report With a Human-Written Case Report: Practical Considerations for AI-Assisted Medical Writing.Cureus. 2024 May 16;16(5):e60461. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60461. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38883028 Free PMC article.
-
The Expanding Role of ChatGPT (Chat-Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) in Neurosurgery: A Systematic Review of Literature and Conceptual Framework.Cureus. 2023 Aug 15;15(8):e43502. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43502. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37719492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ChatGPT in medicine: A cross-disciplinary systematic review of ChatGPT's (artificial intelligence) role in research, clinical practice, education, and patient interaction.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Aug 9;103(32):e39250. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039250. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39121303 Free PMC article.
-
The Intersection of ChatGPT, Clinical Medicine, and Medical Education.JMIR Med Educ. 2023 Nov 21;9:e47274. doi: 10.2196/47274. JMIR Med Educ. 2023. PMID: 37988149 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the accuracy of ChatGPT's responses to and references for clinical questions in physical therapy.J Phys Ther Sci. 2024 May;36(5):234-239. doi: 10.1589/jpts.36.234. Epub 2024 May 1. J Phys Ther Sci. 2024. PMID: 38694019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atypia predicting prognosis for intracranial extraventricular neurocytomas. Kane AJ, Sughrue ME, Rutkowski MJ, et al. J Neurosurg. 2012;116:349–354. - PubMed
-
- Extraventricular neurocytoma, a comprehensive review. Patil AS, Menon G, Easwer HV, Nair S. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2014;156:349–354. - PubMed
-
- Patterns of care and survival outcomes in patients with an extraventricular neurocytoma: an individual patient data analysis of 201 cases. Mallick S, Benson R, Rath GK. Neurol India. 2018;66:362–367. - PubMed
-
- ChatGPT: five priorities for research. van Dis EA, Bollen J, Zuidema W, van Rooij R, Bockting CL. Nature. 2023;614:224–226. - PubMed
-
- Abstracts written by ChatGPT fool scientists. Else H. Nature. 2023;613:423. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
