Application of a Dermal Regeneration Matrix for the Surgical Treatment of an Oromaxillary Defect in Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
- PMID: 37033567
- PMCID: PMC10075332
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.35833
Application of a Dermal Regeneration Matrix for the Surgical Treatment of an Oromaxillary Defect in Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Abstract
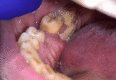
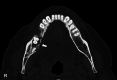
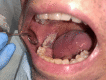
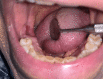
Surgical options for managing patients with medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw are multiple and may range from superficial debridement to vascularized osteocutaneous free flaps. However, some protocols may not be an option in specific cases, and alternative techniques for patients who are not likely candidates for more invasive procedures may represent a suitable solution to treat these patients. Here, we report the case of a 69-year-old man who presented to the Stomatology Department with dysphagia, exposed bone, and mild mandibular pain for the past three months. The patient was diagnosed with stage III medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Surgical debridement with sequestrum removal was performed and the remaining intraoral defect, which was unsuitable for primary closure, was addressed with a dermal regeneration matrix. This system allowed full coverage of the surgical wound. At 10 weeks of follow-up, the intraoral defect had healed completely with no need for active intervention. Dermal regeneration matrixes may represent a surgical approach to cover oromaxillary defects in select patients.
Keywords: bisphosphonates; dermal regeneration matrix; jaw osteonecrosis; mronj; oromaxillary defect.
Copyright © 2023, Seixas et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Adjuvant therapies for MRONJ: a systematic review. Govaerts D, Piccart F, Ockerman A, Coropciuc R, Politis C, Jacobs R. Bone. 2020;141:115676. - PubMed
-
- Use of Integra® dermal regeneration template and flowable matrix to reconstruct an oral cavity defect involving the nasal floor. Mumtaz S, Patel H, Singh M. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;58:0–4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
