Development, testing, parameterisation, and calibration of a human PBK model for the plasticiser, di (2-ethylhexyl) adipate (DEHA) using in silico, in vitro and human biomonitoring data
- PMID: 37033641
- PMCID: PMC10076754
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1165770
Development, testing, parameterisation, and calibration of a human PBK model for the plasticiser, di (2-ethylhexyl) adipate (DEHA) using in silico, in vitro and human biomonitoring data
Abstract
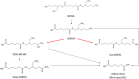
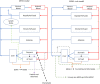
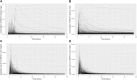
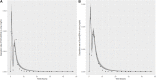
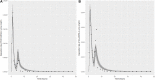
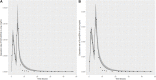
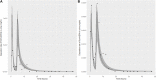
Introduction: A physiologically based biokinetic model for di (2-ethylhexyl) adipate (DEHA) based on a refined model for di-(2-propylheptyl) phthalate (DPHP) was developed to interpret the metabolism and biokinetics of DEHA following a single oral dosage of 50 mg to two male and two female volunteers. Methods: The model was parameterized using in vitro and in silico methods such as, measured intrinsic hepatic clearance scaled from in vitro to in vivo and algorithmically predicted parameters such as plasma unbound fraction and tissue:blood partition coefficients (PCs). Calibration of the DEHA model was achieved using concentrations of specific downstream metabolites of DEHA excreted in urine. The total fractions of ingested DEHA eliminated as specific metabolites were estimated and were sufficient for interpreting the human biomonitoring data. Results: The specific metabolites of DEHA, mono-2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl adipate (5OH-MEHA), mono-2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl adipate (5oxo-MEHA), mono-5-carboxy-2-ethylpentyl adipate (5cx-MEPA) only accounted for ∼0.45% of the ingested DEHA. Importantly, the measurements of adipic acid, a non-specific metabolite of DEHA, proved to be important in model calibration. Discussion: The very prominent trends in the urinary excretion of the metabolites, 5cx-MEPA and 5OH-MEHA allowed the important absorption mechanisms of DEHA to be modelled. The model should be useful for the study of exposure to DEHA of the general human population.
Keywords: DEHA; PBPK; in silico; plasticiser; reverse dosimetry.
Copyright © 2023 McNally, Sams and Loizou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Barter Z. E., Bayliss M. K., Beaune P. H., Boobis A. R., Carlile D. J., Edwards R. J., et al. (2007). Scaling factors for the extrapolation of in vivo metabolic drug clearance from in vitro data: Reaching a consensus on values of human microsomal protein and hepatocellularity per gram of liver. Curr. Drug Metab. 8 (1), 33–45. 10.2174/138920007779315053 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barton H. A., Bessems J., Bouvier d'Yvoire M., Buist H., Clewell H., III, Gundert-Remy U., et al. (2009). Principles of characterizing and applying physiologically-based pharmacokinetic and toxicokinetic models in risk assessment. Geneva: World Health Organization.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

