Traditional Chinese medicine in treating ischemic stroke by modulating mitochondria: A comprehensive overview of experimental studies
- PMID: 37033646
- PMCID: PMC10073505
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1138128
Traditional Chinese medicine in treating ischemic stroke by modulating mitochondria: A comprehensive overview of experimental studies
Abstract
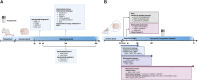
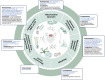
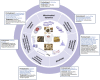
Ischemic stroke has been a prominent focus of scientific investigation owing to its high prevalence, complex pathogenesis, and difficulties in treatment. Mitochondria play an important role in cellular energy homeostasis and are involved in neuronal death following ischemic stroke. Hence, maintaining mitochondrial function is critical for neuronal survival and neurological improvement in ischemic stroke, and mitochondria are key therapeutic targets in cerebral stroke research. With the benefits of high efficacy, low cost, and high safety, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has great advantages in preventing and treating ischemic stroke. Accumulating studies have explored the effect of TCM in preventing and treating ischemic stroke from the perspective of regulating mitochondrial structure and function. In this review, we discuss the molecular mechanisms by which mitochondria are involved in ischemic stroke. Furthermore, we summarized the current advances in TCM in preventing and treating ischemic stroke by modulating mitochondria. We aimed to provide a new perspective and enlightenment for TCM in the prevention and treatment of ischemic stroke by modulating mitochondria.
Keywords: ischemic stroke; mitochondria; molecular mechanism; review; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Chen, Zhou, Yuan, Chen, Sun, Zhou, Liu, Sun, Chen and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- An H., Tao W., Liang Y., Li P., Li M., Zhang X., et al. (2021). Dengzhanxixin injection ameliorates cognitive impairment through a neuroprotective mechanism based on mitochondrial preservation in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 712436. 10.3389/fphar.2021.712436 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

