Pharmacokinetic comparison of sitagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release tablets versus JANUMET® XR in healthy volunteers under fasting and fed conditions
- PMID: 37033652
- PMCID: PMC10073488
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1105767
Pharmacokinetic comparison of sitagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release tablets versus JANUMET® XR in healthy volunteers under fasting and fed conditions
Abstract
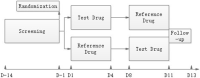
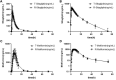
Background and Objectives: Janumet® XR is the combination of sitagliptin and extended metformin hydrochloride produced by Merck Sharp & Dohme. It is specially designed for diabetes mellitus patients taking both drugs already. Janumet® XR exhibited clinically significant blood glucose lowering efficacy and long-term use safety. However, no generic form of Janumet® XR has been approved in western countries. The relatively high cost made the medication less prescribed. A more affordable form of this drug may benefit an immense diabetes mellitus population. The current study compared the bioequivalence (BE) of sitagliptin 100 mg and metformin 1000 mg produced by Nanjing Chia-Tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Company to Janumet® XR in healthy Chinese subjects. Methods: Twenty-eight healthy Chinese subjects were enrolled in Study 1 and 2, respectively. Both studies were conducted with an open, randomized, two-period crossover design using the test (T) or the reference (R) drug. Study 1 is conducted under the fasting state, and Study 2 is under the fed state. Subjects received an oral dose of sitagliptin 100 mg and metformin 1000 mg, and plasma concentrations of sitagliptin and metformin were determined up to 72 h post-dose. Pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters, including maximum serum concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration-time curve up to the last quantifiable concentration (AUC0-t) of both sitagliptin and metformin, were calculated and compared between the T and R treatments. Results: In the fasting study, the geometric mean ratios of Cmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-∞ for sitagliptin were 109.42%, 101.93%, and 101.95%, respectively; the corresponding ratios for metformin were 98.69%, 94.12%, and 93.42%, respectively. In the fed study, the geometric mean ratios of Cmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-∞ for sitagliptin were 98.41%, 100.30%, and 100.24%, respectively; the corresponding ratios for metformin were 97.79%, 99.28%, and 100.69%, respectively. The 90% CIs of Cmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-∞ in both studies were all within acceptance limits (80.00%-125.00%). Conclusion: The results demonstrated for the first time that sitagliptin 100 mg and metformin 1000 mg produced by Nanjing Chia-Tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Company was bioequivalent to the branded Janumet® XR, and both drugs were well tolerated.
Keywords: Janumet® XR; bioequivalence; diabetes; metformin; pharmacokinetics; sitagliptin.
Copyright © 2023 Que, Qin, Shi, Ding, Huang, Qian, Huang, Zhou and He.
Conflict of interest statement
BH and PZ were employed by the Nanjing Chia-Tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmed A., Wasim A. A., Fazal-Ur-Rehman S., Ali M. (2022). Development of extended-release metformin core tablet and synergistic coating of sitagliptin for the treatment of type-II diabetes mellitus - a comparative drug release evaluation with reference product. Pak J. Pharm. Sci. 35 (5), 1473–1480. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed I., Raja U. Y., Wahab M. U., Rehman T., Ishtiaq O., Aamir A. H., et al. (2022). Efficacy and safety of combination of empagliflozin and metformin with combination of sitagliptin and metformin during ramadan: An observational study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 22, 247. 10.1186/s12902-022-01168-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Kuraishy H. M., Al-Gareeb A. I., Albogami S. M., Jean-Marc S., Nadwa E. H., Hafiz A. A., et al. (2022). Potential therapeutic benefits of metformin alone and in combination with sitagliptin in the management of type 2 diabetes patients with COVID-19. Pharmaceuticals 15, 1361. 10.3390/ph15111361 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arechavaleta R., Seck T., Chen Y., Krobot K. J., O'Neill E. A., Duran L., et al. (2011). Efficacy and safety of treatment with sitagliptin or glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy: A randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 13 (2), 160–168. 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01334.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

