One-Step Fabrication of the ZnO/g-C3N4 Composite for Visible Light-Responsive Photocatalytic Degradation of Bisphenol E in Aqueous Solution
- PMID: 37033806
- PMCID: PMC10077555
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c06678
One-Step Fabrication of the ZnO/g-C3N4 Composite for Visible Light-Responsive Photocatalytic Degradation of Bisphenol E in Aqueous Solution
Abstract
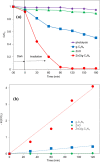
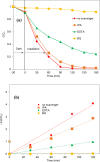
The ZnO/g-C3N4 composite was successfully synthesized by a simple one-step calcination of a urea and zinc acetate mixture. The photocatalytic activity of the synthesized composite was evaluated in the degradation of bisphenol E (BPE). The morphology, crystallinity, optical properties, and composition of the synthesized composite were characterized by using various analytical techniques such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmitted electron microscopy (TEM), field emission-electron probe microanalysis (FE-EPMA), nitrogen adsorption and desorption isotherm measurement, Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS), photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The degradation rate of BPE with the ZnO/g-C3N4 composite was 8 times larger than that obtained with pure g-C3N4 at the optimal conditions. The excellent photocatalytic activity was attributed to the synergistic effect between the g-C3N4 and ZnO, which enhanced the efficiency of charge separations, reduced the e-/h+ pairs recombination, and increased the visible light absorption ability. The radical scavenger studies indicated that the •O2 - and h+ species were mainly responsible for the degradation of BPE. The stability test suggested the chemical and photostability of the synthesized composite. Two possible photocatalytical mechanisms have been suggested.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Savage P. E.; Hunter S. E.; Hoffee K. L.; Schuelke T. J.; Smith M. J. Bisphenol E Decomposition in High-Temperature Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 7775–7780. 10.1021/ie060888l. - DOI
-
- Garg R.; Gupta R.; Bansal A. Synthesis of g-C3N4/ZnO Nanocomposite for Photocatalytic Degradation of a Refractory Organic Endocrine Disrupter. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 855–859. 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.787. - DOI
-
- Uzzaman M.; Hasan M. K.; Mahmud S.; Yousuf A.; Islam S.; Uddin M. N.; Barua A. Physicochemical, Spectral, Molecular Docking and ADMET Studies of Bisphenol Analogues; A Computational Approach. Inf. Med. Unlocked 2021, 25, 10070610.1016/j.imu.2021.100706. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

