Exploration of Antiproliferative Activity and Apoptosis Induction of New Nickel(II) Complexes Encompassing Carbazole Ligands
- PMID: 37033823
- PMCID: PMC10077545
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c01252
Exploration of Antiproliferative Activity and Apoptosis Induction of New Nickel(II) Complexes Encompassing Carbazole Ligands
Abstract
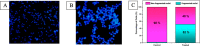
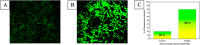
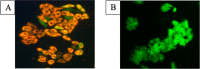
To attest the effectiveness of nickel complexes as anticancer drug candidates with minimum side effects, the present investigation describes the facile synthesis and anticancer activities of nickel(II) complexes enriched with three derivatives of carbazolone-based benzhydrazone ligands(L) having a [Ni(L)2] composition. Analytical and spectral techniques were used to characterize the synthesized Ni(II) complexes. The single-crystal X-ray diffraction performed for complex 4 confirmed the square planar geometry with a [Ni(κ2-N,O-L)2] arrangement. The MTT assay was carried out for the complexes to determine in vitro cytotoxicity against cancerous human-cervical carcinoma, human-colon carcinoma, and non-cancerous L929 (fibroblast) cells. All three complexes exhibited good toxicity against the cancer cells with a low IC50 concentration. Complex 4, containing -OCH3 fragment, exhibits high lipophilicity and revealed exceptional cytotoxicity against cancer cells. AO-EB fluorescent staining indicated apoptosis-associated cell morphological changes after exposure to complex 4. The apoptosis induction was further confirmed by a HOECHST-33342 fluorescent staining technique via chromosomal condensation and nuclear fragmentation. Further, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) mechanistic studies revealed that complex 4 can raise ROS levels and reduce MMP and promote mitochondrial dysfunction-mediated apoptotic cell death. Further, stimulation of late apoptosis by complex 4 in cervical cancer cells was quantitatively differentiated through the staining of phosphatidylserine externalization by flow cytometry. Furthermore, the ELISA analysis confirmed that complex 4 induced apoptosis through caspase activation.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Investigation into antiproliferative activity and apoptosis mechanism of new arene Ru(ii) carbazole-based hydrazone complexes.Dalton Trans. 2020 Aug 18;49(32):11385-11395. doi: 10.1039/d0dt01476a. Dalton Trans. 2020. PMID: 32776042
-
Ni(II) curcumin complexes for cellular imaging and photo-triggered in vitro anticancer activity.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Oct 15;204:112632. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112632. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32781350
-
DNA binding, cleavage and cytotoxicity studies of three mononuclear Cu(II) chloro-complexes containing N-S donor Schiff base ligands.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2018 Dec;23(8):1331-1349. doi: 10.1007/s00775-018-1620-2. Epub 2018 Oct 9. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2018. PMID: 30302601
-
Induction of cell death by ternary copper(II) complexes of L-tyrosine and diimines: role of coligands on DNA binding and cleavage and anticancer activity.Inorg Chem. 2009 Feb 16;48(4):1309-22. doi: 10.1021/ic801144x. Inorg Chem. 2009. PMID: 19140687
-
Synthesis of Ni(II) complexes bearing indole-based thiosemicarbazone ligands for interaction with biomolecules and some biological applications.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2017 Jun;22(4):461-480. doi: 10.1007/s00775-016-1424-1. Epub 2016 Dec 19. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2017. PMID: 27995332
Cited by
-
Hypericum empetrifolium and H. lydium as Health Promoting Nutraceuticals: Assessing Their Role Combining In Vitro In Silico and Chemical Approaches.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Mar 31;13(4):e70053. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70053. eCollection 2025 Apr. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40171554 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of In Vitro Anticancer Activity and Apoptotic Potential of Wrightia Tinctoria Bark Extracts on Oral Cancer Cell Lines.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025 May 1;26(5):1753-1759. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2025.26.5.1753. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025. PMID: 40439388 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of novel N-(2-(pyrazin-2-yl-oxy)ethyl)-4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzamide scaffolds, and biological evaluation and molecular docking studies.RSC Adv. 2025 May 23;15(22):17290-17301. doi: 10.1039/d5ra00879d. eCollection 2025 May 21. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40416640 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

