The m6A methylation landscape, molecular characterization and clinical relevance in prostate adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 37033963
- PMCID: PMC10076583
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1086907
The m6A methylation landscape, molecular characterization and clinical relevance in prostate adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Despite the recent progress of therapeutic strategies in treating prostate cancer (PCa), the majority of patients still eventually relapse, experiencing dismal outcomes. Therefore, it is of utmost importance to identify novel viable targets to increase the effectiveness of treatment. The present study aimed to investigate the potential relationship between N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modification and PCa development and determine its clinical relevance.
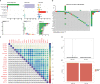
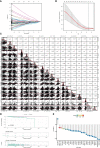
Methods: Through systematic analysis of the TCGA database and other datasets, we analyzed the gene expression correlation and mutation profiles of m6A-related genes between PCa and normal tissues. Patient samples were divided into high- and low-risk groups based on the results of Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) Cox analysis. Subsequently, differences in biological processes and genomic characteristics of the two risk groups were determined, followed by functional enrichment analysis and gene set enrichment (GSEA) analysis. Next, we constructed the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of differentially expressed genes between patients in high- and low-risk groups, along with the mRNA-miRNA-lncRNA network. The correlation analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells was further conducted to reveal the differences in immune characteristics between the two groups.
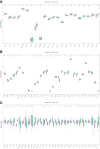
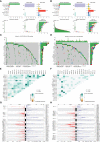
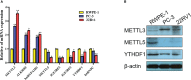
Results: A variety of m6A-related genes were identified to be differentially expressed in PCa tissues as compared with normal tissues. In addition, the PPI network contained 278 interaction relationships and 34 m6A-related genes, and the mRNA-miRNA-lncRNA network contained 17 relationships, including 91 miRNAs. Finally, the immune characteristics analysis showed that compared with the low-risk group, the levels of M1 and M2 macrophages in the high-risk group significantly increased, while the levels of mast cells resting and T cells CD4 memory resting significantly decreased.
Conclusions: This study provides novel findings that can further the understanding of the role of m6A methylation during the progression of PCa, which may facilitate the invention of targeted therapeutic drugs.
Keywords: RNA N6-methyladenosine; immune infiltration; molecular characterization; prognosis; prostate adenocarcinoma.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Peng, Gan, Zhou, Hou, Wang, Yuan, Xiong and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
N6-methyladenosine-related lncRNAs identified as potential biomarkers for predicting the overall survival of Asian gastric cancer patients.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jul 1;22(1):721. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09801-z. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35778697 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of tumor immune microenvironment and prognosis of m6A-related lncRNAs in gastric cancer.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 24;22(1):316. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09377-8. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35331183 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of m6A-Related Signatures in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Identification of Clinical Prognostic Regulators in Adrenocortical Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 3;12:637933. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.637933. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33746977 Free PMC article.
-
N6-Methyladenosine Modification Patterns and Tumor Microenvironment Immune Characteristics Associated With Clinical Prognosis Analysis in Stomach Adenocarcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 15;10:913307. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.913307. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35813200 Free PMC article.
-
The functional roles of m6A modification in prostate cancer.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2023 Nov;17(6):e2200108. doi: 10.1002/prca.202200108. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2023. PMID: 37070355 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunomodulatory role of RNA modifications in sex hormone-dependent cancers.Front Immunol. 2025 May 8;16:1513037. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1513037. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40406121 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

